FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
Layer 2 tunneling protocol (L2TP) is a VPN technology that connects two computers over a network connection. It works with any type of internet connection, including dial-up, DSL, cable modem, and wireless networks.
You should learn how layer-2 tunneling protocols work to get the most from your network connection. It will help you save bandwidth, speed up your internet connections, and even make your computer run cooler.
This tutorial will teach you everything you need to know about layer-2 tunneling protocol (L2TP).
Further, this article will show you the comparison between L2TP works and other protocols.
The L2TP protocol was developed by Cisco Systems and has become very popular among businesses because it provides security and privacy while allowing remote employees to work from home.
We have created this tutorial to help you get started with L2TP connections. We hope you find it useful!
What is Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2PT)?
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (LT2T) is an extension of Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol (PPTP) used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provide VPN connections. LT2T uses a secure tunneling mechanism that encrypts the entire packet exchange between the client and the server.
To ensure security and privacy, LT2T must rely on an encryption algorithm to pass within the tunnel; therefore, it cannot use standard PPTP encryption methods such as DES/3DES or RC4. Instead, LT2T relies on the strong AES cipher.
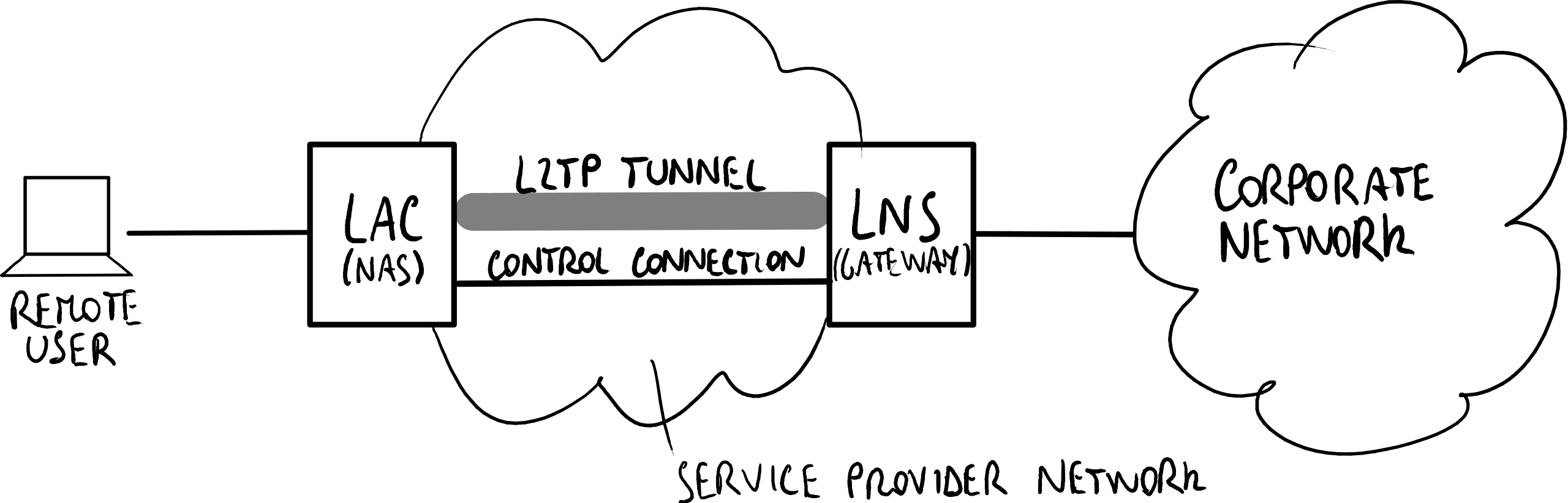
The process initiates a tunnel from an Access Concentrator (LC) to a Network Server (LS) on the Internet. This enables a point-to-point (PPP) link level encapsulated and transmitted across the Internet.
The end user initiates a dial-up connection to an ISP through ISDN or Public Switched Telephone Network (PSNT).
What is L2TP used for?
L2TP stands for Layer-2 Tunneling Protocol. It is a standard protocol designed to provide secure communications over dial-up networks. This allows you to send data across the Internet without encryption.
The basic idea behind L2TP is simple. You connect to a remote computer via a dial-up modem. When you make a call, the telephone line splits into two paths.
One path goes directly to the destination phone number, while the second path connects to the remote computer. A layer-2 tunnel is established between the two computers allowing one side to see the traffic coming from the other side.
L2TP does not require special hardware. It works well on most modems. It works best when both sides support L2TP because the software automatically negotiates the correct parameters for the tunnel.
L2TP protocol allows remote access to smartphones, tablets, laptops, printers, or routers. In addition, it enables multiple simultaneous sessions and supports encryption.
The main advantage of using L2TP is Ethernet encapsulation, which makes it compatible with existing IP networks. Therefore, you don’t need to change your infrastructure. You just need to install L2TP on your device.
In addition, L2TP offers several advantages compared to PPTP. For example, you can use it to provide VPN connectivity to mobile devices without requiring special hardware.
Moreover, L2TP doesn’t require specific software on the client side. And finally, it’s easier to configure because there are fewer settings.
How does L2TP differ from PPTP?
L2TP stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol. This protocol allows you to connect two computers together securely without requiring the use of a router. You can use it to set up VPN connections, secure remote access solutions, and even peer-to-peer applications such as BitTorrent.
PPTP stands for Point-To-Point Tunneling Protocol. This technology works similarly to L2TP, except it requires a third computer called a PPP server to establish the connection. A PPP server acts like a gateway between two clients.
The main difference between L2TP and PPT is that L2TP uses UDP while PPT uses TCP. Both protocols support multiple simultaneous sessions. However, L2TP offers more flexibility because it can use compression or encryption to reduce overhead.
Compression reduces the size of packets sent across a network. Encryption adds security to data transmitted via a network.
What are the Layer 2 protocols?
Many Layer 2 communication protocols are used by L2 devices, including multiport bridges and network interface cards. These protocols allow data to travel between nodes in a LAN or across a Wide Area Network (WAN).
Some of the most common protocols include:
- Multipoint Control Unit Protocol (MCUP);
- Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP);
- Point-To-Multipoint Tunneling Protocol (PTMTP);
- Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE);
- Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP).
What are Layer-2 Tunneling Protocol features?
L2TP is a protocol used to secure packet communications over Point-to-Point connections. There are many different versions of L2TP, including PPTP, MSCHAPv2, EAP-MSCHAPv2, PEAP, RADIUS, etc., but L2TP stands out because it provides both authentication and encryption.
The most common use case for L2TP is VPN access. However, there are numerous other uses, such as remote access, network security, and Internet connectivity.
In addition, L2TP is commonly used in conjunction with IPSec. When combined together, these protocols provide strong security while ensuring that data cannot be intercepted during transmission.
What is L2TP passthrough?
L2TP passthrough allows you to connect multiple Internet devices without static IP addresses. You can set up VPN connections over L2TP/IPsec tunnels, allowing you to access resources behind firewalls and NAT routers securely. This article provides a brief introduction to L2TP passthrough and how it works.
What is TCP tunneling?
TCP tunneling allows you to send traffic over multiple IP addresses through one port on your router. This method makes it possible to use a single IP address for many different applications.
For example, you could connect a VPN client to a remote server while connecting a web browser to a local network resource.
If you are running both applications on a single computer, there is no way to do this without TCP tunneling because each application must bind to a separate IP address.
What is L2TP over IPsec?
L2TP over IPsec is one of many ways to connect devices together securely. It allows you to use Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), which lets you send data across networks without going through routers.
Connecting two computers, phones, tablets, or other devices makes it easy.
You don’t need to worry about configuring network settings or getting into complicated configurations. But there are some things you need to know before you proceed.
What is an L2TP secret?
An L2TP secret is a unique password you use in place of a normal password to log into a VPN connection.
This type of password is required because PPTP uses the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), a protocol developed by Microsoft.
To connect to a PPTP server, you need a special password called an L2TP secret, which is different from the standard username and password combination.
How Good Is L2TP Security?
While many people consider L2TP tunneling to be a better VPN option than PPTP, there are some things you should know about it. For starters, L2TP doesn’t encrypt anything; rather, it pairs up with another protocol called IPsec.
This way, even though L2TP isn’t technically encrypted, it still provides strong security because of the added layer of protection offered by IPSec. L2TP/IPSec is considered one of the most secure VPN protocols.
The reason why you might want to use L2TP/IPSEC, however, is because it offers a lot of benefits over PPTP. First off, it’s much faster. You’ll notice this, especially when connecting to servers outside your home network.
Because L2TP/IPSec does everything in one fell swoop, it can connect to remote servers much more quickly than PPTP.
Another benefit of L2TP/IPSec is that it works across multiple operating systems. With PPTP, you’d have to choose whether you wanted to use Windows or Linux. However, with L2TP/IPSC, you don’t have to worry about that.
So, if you use Windows 7, 8, 10, Android, iOS, macOS, or Linux, you can still enjoy the same level of security and speed.
While L2TP/IPSec is great, it’s not perfect. There are ways around it. One of those ways is by using a proxy server. A proxy server acts as a middleman between your computer and the Internet.
By doing this, you can bypass the L2TP/IPSec process altogether. Use a reputable proxy provider if you decide to go down this route. Otherwise, you could end up getting infected by malware.
How Fast Is L2TP?
L2TP stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol, and it’s one of many protocols used in VPNs. This particular protocol is often referred to as “PPPoE,” which stands for Point-to-Point Over Ethernet. PPPoE works just like traditional dial-up internet access, except that it uses IP packets rather than phone lines.
The problem with L2TP is that it doesn’t encrypt data. While this isn’t a big deal for most people, someone else could intercept your traffic.
In addition, even if you’re using an encrypted tunnel, there’s no guarantee that your ISP won’t monitor your activity.
However, L2TP offers better throughput than PPTP because it uses UDP, which is much faster than TCP. For example, I’ve seen a couple of hundred megabits per second transferred over L2TP.
However, those numbers are based on my home network, where everything runs smoothly. You’ll probably see lower speeds if you transfer large amounts of data across a slower connection.
How Easy Is It to Set Up L2TP?
L2TP is one of many protocols to secure Internet traffic over public networks like Wi-Fi hotspots, mobile data connections, and even Ethernet cables. If you’re looking to connect to a remote network via a VPN tunnel, L2TP is probably what you want to use.
On most Windows and macOS devices, it’s as simple as going into your Network Settings and following a few steps.
In addition to being easy to set up, L2TP is relatively straightforward to implement too. Most routers come preconfigured with the necessary settings already, and there aren’t any additional configuration options you’ll need to worry about.
The only real downside to L2TP is that it doesn’t work out of the box on some older hardware platforms, including Android phones and tablets.
However, it’s still possible to switch to L2TP without buying a new device. All you need is a little know-how and patience.
What Is an L2TP VPN?
L2TP stands for Layer Two Tunneling Protocol. This protocol is used to tunnel network traffic over IPsec tunnels. A VPN server uses the L2TP protocol to connect to remote clients.
When a client connects to a VPN server, it opens a connection to the server using the L2TP protocol, and then the client establishes an IPSec tunnel to the server.
Once the IPSec tunnel is established, the client can send and receive data securely across the Internet without worrying about eavesdroppers intercepting the data.
Advantages and disadvantages of L2TP
The main advantage of L2TP is that it offers a good level of online security. This is because it encrypts data in transit, meaning no one else can see it. It doesn’t do anything about eavesdroppers, so you still need to use strong passwords and keep your network safe.
Another advantage is that it’s widely supported across most OSes and devices. You don’t need to worry about compatibility issues.
If you’re using Windows 7 or later, chances are that you already have it installed. If you’re using a Mac, you’ll find that Apple includes it in newer versions of OS X. And if you’re using Linux or BSD, there are plenty of third-party solutions.
However, L2TP has some disadvantages. For one thing, L2TP is unencrypted, meaning anyone monitoring traffic could see what sites are visited and even snoop around inside your network.
Additionally, L2TP isn’t very scalable because each packet needs to travel twice over the physical layer to reach the destination device and return to the source. This makes L2TP a little slower than most VPN protocols. However, L2TP does support IPv6, which many people find appealing.
The biggest disadvantage of L2TP is that it requires both L2TP and IPSec to work correctly. If you’re connecting to a server that uses L2TP without IPSec, you won’t be able to browse securely.
To make matters worse, if someone manages to crack L2TP, they’ll have full access to your entire network.
Comparison between L2TP and Other VPN Protocols
This section compares L2TP/IPsec to other VPN protocols. By itself, L2TP does not protect against eavesdropping, so most VPN providers add another layer of encryption called IPSec.
When you normally hear a VPN provider talk about the L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) protocol and say it provides access to it, they mean L2TP/IPSec.
Comparison between L2TP and PPTP
PPTP stands for Point-to-Point Tunneled Protocol. This is one of the most widely used protocols for creating VPN connections. While it does provide some advantages over L2TP, it doesn’t offer nearly as many.
L2TP provides better security than PPTP because it uses IPsec (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol). IPSec is generally considered to be far more secure than PPTP, especially when it comes to protecting against eavesdropping.
Moreover, PPTP supports only 128-bit encryption, whereas L2TP supports up to 256 bits. This makes PPTP less secure than L2TP.
Also, PPTP is pretty slow. It typically takes around 30 seconds to establish a connection, while L2TP is usually established within just a few milliseconds.
Since PPTP runs over TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol), it’s easier to detect and block. Firewalls are explicitly designed to prevent traffic from coming into the network. If you’re using a firewall, it won’t allow PPTP traffic.
On the other hand, L2TP runs over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Because it’s a lower-level protocol, it’s harder for a firewall to detect and more difficult to block.
As mentioned earlier, L2TP can run over different kinds of encryption. PPTP cannot do this.
Comparison between L2TP and IKEv2
IKEv2 is a protocol for creating secure connections between devices such as computers and mobile phones.
Regarding VPN protocols, IKEv2 stands out because it provides better performance and reliability than L2TP. However, some people still prefer L2TP because it’s easier to set up and use, while others like IKEv2 because it offers greater privacy.
Microsoft and the networking giant Cisco developed IKEv2, based on IPSec, the protocol we know today as IPsec.
So what exactly is IKEv2, and how does it work? Well, IKEv2 uses a tunneling protocol called Tunnel Mode Security Association Protocol (TMSAP), a combination of IPSec and Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP).
This way, IKEv2 enables the creation of secure tunnels between two points. The protocol supports mobility and multihoming, which works even when the device isn’t directly connected to the Internet.
To sum things up, here are the main differences between IKEv2 and L2TP:
- With IKEv2, connecting to multiple networks is possible, whereas with L2TP, you’re limited to one network.
- You don’t need to configure IKEv2, unlike with L2TP manually; however, it’s important to note that both protocols require manual configuration to enable encryption.
- With IKE v2, you can easily change your local network settings, whereas, with L2tp, you need to reconfigure the client manually.
- With IKEv2, you can choose whether to encrypt traffic sent or received.
- And finally, with IKEv 2, you don’t need to install third-party software.
Comparison between L2TP and OpenVPN
Both L2TP and OpenVPN are VPN protocols. They encrypt data packets sent over the Internet, ensuring privacy while allowing remote access to networks.
But some key differences between the two protocols make one better suited for certain situations than the other.
The biggest difference is speed. While most people think of encryption as being slow, it isn’t. OpenVPN is faster than L2TP.
This makes OpenVPN perfect for connecting to public Wi-Fi hotspots, where bandwidth is often limited. Conversely, L2TP works well on wired connections, where bandwidth isn’t usually an issue.
Another advantage of OpenVPN is that it supports multiple protocols. For example, it can connect to standard IPsec tunnels, such as those used by Windows XP and Vista systems. And it can even support IPSec tunnels, which allow secure communications over UDP/IPv4.
While we’ve mentioned the advantages of OpenVPN above, remember that there are disadvantages too.
One drawback is that OpenVPN doesn’t work on every device. Some devices don’t support the protocol, and others require special configuration steps.
Also, OpenVPN requires a lot of manual setups. You’ll need to manually download and install the software, configure it, and test it out. If something goes wrong, you’ll have to start again.
On the other hand, L2TP is much easier to set up. You run a few commands, and the rest happens automatically. Plus, L2TP is supported by almost every operating system, making it easy to find compatible clients.
There are many other factors to consider when choosing between L2TP and OpenVPN. The best way to decide what’s right for you is to try each protocol out.
Start with L2TP, and see how things go. Then switch to OpenVPN, and compare the experience. Once you’ve done that, you’ll know whether either of these protocols is right for you.
Comparison between L2TP and SSTP
L2TP and SSTP (Secure Shell Tunneling Protocol) are VPN protocols that connect remote clients to a network via a virtual private network server.
They both encrypt data traffic and allow users to access resources securely over public networks such as the Internet. However, while L2TP is supported on most modern devices, SSTP is only found on Windows OSes.
The main difference between L2TP and SSPT is how they handle encryption. While L2TP encrypts every packet sent across the connection, SSTP only encrypts packets that travel within the tunnel. This makes SSTP much faster than L2TP since it doesn’t require extra processing power to decrypt each packet.
However, SSTP isn’t compatible with many routers and firewalls, whereas L2TP works well with almost any device. Because of this, L2TP tends to be preferred over SSTP.
Comparison between L2TP and WireGuard®
WireGuard isn’t just another VPN solution; it offers much more than most people think about virtual private networks. There are many reasons why WireGuard is better than L2TP/IPsec. Here are some of those reasons.
1. Security
While both protocols provide encryption, WireGuard does it differently. With L2TP/IPSEC, the entire connection is encrypted, including the control channel.
This means that anyone sniffing traffic could potentially see everything sent over the wire. With WireGuard, however, the control channel is protected by end-to-end encryption.
2. Performance
When it comes to performance, WireGuard beats L2TP/IPsec hands down. While L2TP/IPSec requires multiple TCP connections to work properly, WireGuard needs only one UDP packet per connection.
3. Open Source
WireGuard is open-source software. As such, it’s much easier to audit and verify the code. Plus, it’s free to download and install. On the other hand, L2TP/IPSec is proprietary software and, thus, harder to audit.
Comparison between L2TP and SoftEther
SoftEther offers three protocols: IPsec tunneling via PPTP, L2TP over UDP, and L2TP over TCP. Of course, you don’t have to choose just one.
You can mix and match them. For example, you could start with an IPsec connection and later switch to L2TP. Or you could begin with an L2TP connection and then move to IPsec.
The L2TP protocol itself is pretty simple. It’s used to set up a secure data channel between two hosts.
The security properties are similar to those offered by IPsec; however, there are some differences. One big difference is that L2TP doesn’t require a shared secret.
This makes it easier to implement because no keys need to be exchanged beforehand. Another difference is that the packets are sent unencrypted. However, since L2TP is a layer-2 protocol, it does offer packet fragmentation.
In addition, SoftEther provides a VPN server. While most VPN servers provide only a client application, SoftEther includes a server component.
So, besides providing a VPN client, SoftEther can act as a VPN server. It supports several protocols like IPsec, GRE, VPLS, and MPLS.
Comparison between L2TP and IPSec
VPN providers offering L2TP and IPSec options often advertise the former as “the most secure,” but that’s not necessarily true. While L2TP offers a degree of security over unencrypted traffic, IPSec provides much more protection.
For starters, IPSec is much easier to block with a firewall. L2TP isn’t blocked by default, so users must enable it manually. But even once enabled, L2TP still allows connections to unencrypted sites like Facebook and Twitter, whereas IPSec completely blocks those connections.
Also, IPSec is much more difficult to hack into than L2TP because it requires a hacker to break into the endpoint device. With L2TP, hackers just need to crack the server, which is usually something easy to accomplish.
Finally, IPSec can transport protocols other than IP, such as AppleTalk, DECnet, NetBEUI, OSI level 2, TCP/IPv4, and XNS, while L2TP supports only IP.
Is L2TP a Good VPN Protocol?
L2TP is one of the oldest protocols still in use today. While it isn’t the most modern protocol, it does serve its purpose well enough.
The protocol is fairly simple and easy to implement, making it ideal for home networks. It’s been around since 1997, and Cisco routers even support it.
The protocol is quite secure, but some people don’t like it because of its double encapsulation feature.
Each packet travels twice over the network, once inside the tunnel and again outside of it.
Because of this, it takes longer to transmit data, and it’s less efficient than other protocols. However, it’s still a decent choice for those looking for a reliable, secure connection.
Conclusion
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunnelling Protocol) is a VPN tunneling protocol that is considered to improve upon PPTP.
Many VPN providers offer access to L2TP, but most people don’t realize that L2TP is just a variant of IPSec. You’ll mainly find L2TP offered alongside IPSec rather than L2TP alone.
So what are the advantages of using L2TP over IPSec? Unlike IPSec, L2TP doesn’t require any special client software to work, and it’s generally easier to set up.
However, it suffers slightly from having no encryption, meaning it’s not as secure as IPSec. Also, because L2TP uses double encapsulation, it can cause slow connections.
As for availability, L2TP works natively on Windows and macOS and is pretty simple to configure on other devices. You’ll need to download third-party apps to connect on iOS, Android, Linux, and OS X.