FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
DHCP is an essential tool in a network that ensures that every host in a network is configured well and connected.
Have you ever thought about how IP address and other essential information are assigned to your computer automatically?
It may be possible that you know the method of how to configure a computer in a network. In a small network with 3-4 computers, you can easily assign an IP address and other details.
The problem started when you have more than 100 computers in a network, and you have to do manual configuration.
Additionally, it will take lots of effort and time, and the chances of getting errors would be high.
To resolve such problems, DHCP came into existence.
DHCP simplifies assigning an IP address and other details that needed to get connected in a network.
It doesn’t matter whether it is a small network or a large network like LAN. DHCP automatically configure a host in a network and monitor for any configuration error.
What is DHCP in networking?
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
A DHCP is a network management protocol that automatically assigns an IP address and other information to every host in a network.
It also ensures that every host’s configuration is done correctly, and hosts can now connect to a network.
It will monitor all hosts in a network so that they can communicate efficiently with the other endpoints.
Apart from the IP address, DHCP also assigns Subnet Mask, DNS (Domain Name Server) server, default gateway address, and other relevant configuration parameters needed to connect in a network.
DHCP is defined in RFC (Request for comments) 2131 and 2132, and it was developed and promoted by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
What DHCP is used for?
The prime reason for adopting DHCP is to simplify the management of IP addresses in a network.
It will ensure that no two hosts can have the same IP address. It makes the process automated and error-free.
Hiring any network administrator who can do manual assigning of IP addresses can lead to confusion and errors.
So, automatization through DHCP makes life easier for the user as well as for network administrators.
Main Component of DHCP
DHCP has some major components that are required in the process of configuration.
A basic understanding of these components is needed.
Let’s look into the list:
DHCP Server
DHCP server holds the pool of IP addresses and other configuration information that is requested by the hosts.
Also, the DHCP server is well connected with a networking device that is running DHCP services.
DHCP Client
The DHCP Client is the endpoint that receives IP configuration details from the DHCP server.
The client can be your computer, mobile device, or IoT endpoint.
Moreover, any device that needs to get connected to a network is known as DHCP Client.
Although most of the devices, by default, get configured to receive DHCP information.
IP address pool
The IP address ranges available to get assigned to the DHCP client are known as the IP address pool.
Also, the allocation of the IP address takes place sequentially.
Subnet
Subnet lets you know how many parts of the IP address are allocated to the network and how much to host in a network.
It manages the network and hosts allocation. Moreover, Subnet is one of the most important information needed to configure a network.
Lease
The Lease is a term used in networking to detail how long a DHCP client can hold an IP address.
The lease factor indicates when an IP address will expire and how to renew it.
DHCP Relay
DHCP Relay assist broadcast messages received from DHCP client to reach the DHCP server.
As we know, the router can forward the broadcast messages on the same subnet. But if it has to send in different subnet, then broadcast messages will be discarded by the router.
Thus, to overcome this problem, the DHCP Replay concept was adopted.
With the help of DHCP Relay, you can forward the broadcast messages received from the DHCP client to the DHCP server situated in a different subnet.
Also, the broadcast message will be received by the destination having a MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF: FF and an IP address of 255.255.255.255.
The core function of DHCP Relay is to convert the broadcast message into a Unicast message and forward it to the DHCP server.
How DHCP Works? Step by step process
DHCP works in the application layer of the TCP/IP model.
In this process, DHCP assigns an IP address to the client with a series of messages exchanged between the DHCP server and DHCP client.
These exchanges of messages are also called DHCP conversations or transactions.
Let’s look into the process.
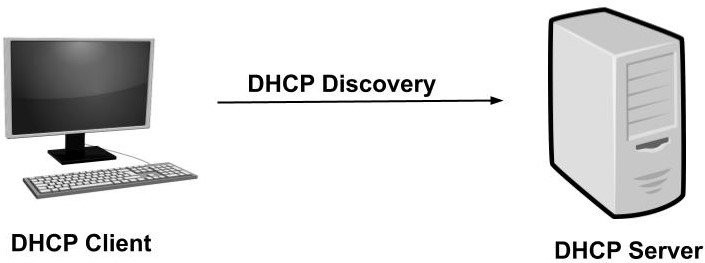
DHCP Discovery
DHCP Discovery is a method in which DHCP client sends broadcast messages to discover the DHCP server in a network.
Moreover, DHCP client’s broadcast message will be received by destination having an IP address of 255.255.255.255, or any specific subnet broadcast address and depends upon how your network was configured.
DHCP offer
When the DHCP client sends a broadcast message and discovers the DHCP server, the DHCP server then sends an offer message offering an IP address from the IP address pool.
The offer message and the proposed IP address also contain the server’s IP address, MAC address of the client, Subnet mask, DNS address, default gateway, and lease information.
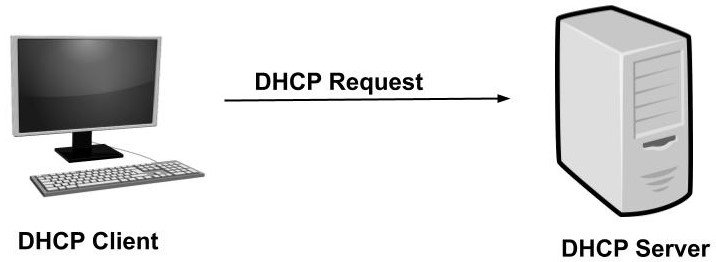
DHCP Request
In a network, there would be the possibility to have more than one DHCP server.
The reason behind having more than one DHCP server is to create a backup for another server if one server fails.
Because of this, the DHCP client can receive more than one DHCP offer, but it has to accept only one DHCP offer.
In response to the offer, the DHCP client has to send a DHCP request to the DHCP server.
Once the DHCP request was accepted, the remaining offered IP address from other DHCP servers will be withdrawn and return to the pool of IP addresses.
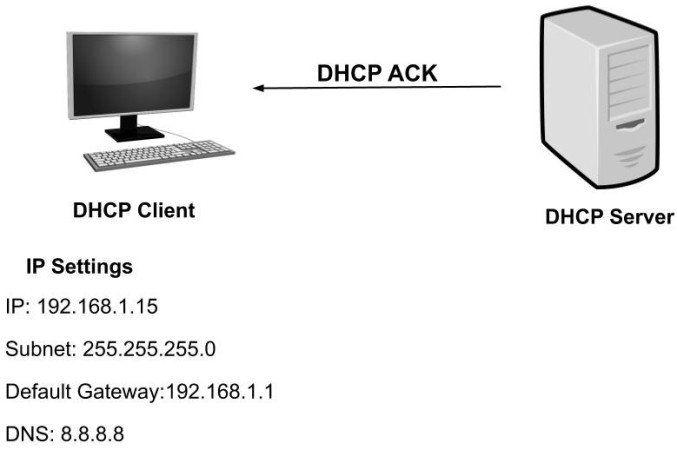
DHCP Acknowledgement
After the DHCP client accepted the DHCP request, the DHCP server sent an acknowledgment known as DHCP Acknowledgement.
DHCP Acknowledgement confirms the DHCP lease to the DHCP client. The DHCP lease will tell the client how long it can hold the current IP address.
This is the final stage of the IP configuration, and now the host is ready to communicate in a network.
DHCP IP address allocation method
To allocate an IP address to the DHCP client, the DHCP server adopts three mechanisms.
Static Allocation
The static allocation is the method in which the DHCP server maintains the allocation table.
The allocation table contains the client’s MAC address and a pool of IP addresses that are to be allocated.
When the client requests an IP address, it will first match the client’s MAC address and then allocate an IP address.
In an organization, the static allocation method is mostly adopted to prevent any unauthorized request.
Dynamic allocation
Dynamic allocation is the method in which IP configuration is allocated to the client for a certain period of time. This is called as lease time.
It will automatically allocate an IP address from the IP address pool and remain valid as per the lease duration.
So, once the lease duration is over, it can request again for another IP address.
Automatic allocation
Unlike dynamic allocation, the automatic allocation method will assign permanent IP configuration on the DHCP client request.
The IP configuration will remain the same indefinitely for the client.
In this case, the DHCP server will set the Lease duration to infinite.
What are the main advantages of using DHCP?
We have already learned that DHCP implied the management of IP configuration, but there are some other benefits of DHCP.
This include:
IP configuration Accuracy
DHCP eases the implementation and automation of the assignment of an IP address.
It maintains the exact parameter of the IP address, and the mistakes are minimized.
Without DHCP, it is challenging to troubleshoot typographical errors.
Minimize IP address conflicts
IP address conflict occurs when one IP address is assigned to more than one computer.
Moreover, the IP address conflict creates a connection problem, and it will become necessary to identify the duplicacy.
This problem occurs mostly in the manual configuration when there are so many hosts in a subnet.
With DHCP, the IP address conflicts are greatly reduced.
Automation in IP address administration
Without DHCP, the IP address administration tasks have to be done manually.
It isn’t easy to keep track of the IP address that is assigned and revoked.
Additionally, it is also difficult to understand when the device needs access to the internet and wants to leave.
In the presence of DHCP, all the processes are centralized and automated. So, it won’t be difficult to trace how far your device is located and track the device’s current status.
Increases efficiency and scope
With DHCP, the assigned IP address can be changed anytime.
In a large organization, where there would be the need to change the pool of IP addresses, it can be changed efficiently.
Also, all configuration information is easily propagated simultaneously to all endpoints of a network.
Similarly, DHCP can handle all types of upgrades and replacement of network devices without any manual intervention.
What are the disadvantages of using DHCP?
Posses greater security risk
The DHCP doesn’t require any authentication from a client to join a network.
So, it will open the risk of the existence of unauthorized servers and unauthorized clients.
Additionally, it will manipulate your information and lead to the depletion of IP addresses because of malicious content originating from the client-side.
As there is no authorization required, the unauthorized server uses the opportunities to provide incorrect network information.
This result in a denial-of-service attack, where an unauthorized server intercepts your data with an intent to spread malicious information.
Also, the unauthorized client can request configuration information from the server on your behalf.
It will then use your credential for malicious purposes and causes the IP addresses’ to exhaust. As a result, you will get disconnected from the network and won’t access the network properly.
Availability of DHCP server
DHCP server plays a major role in a network that assists devices in connecting with the network.
But, if a network contains only one DHCP server, it may create havoc on that server’s failure.
Takeaway
DHCP is a great tool to get auto-configured and remain connected in the network. Also, DHCP is used in IPv4 configuration.
It removes so many hurdles like IP address configuration management, administration, and accuracy.
DHCP increases efficiency and minimizes IP address conflicts.
Besides the benefits of DHCP, the DHCP has certain concerns related to security breaches.
Although some methods are adopted like Static allocation to minimize the security risk, there are still loopholes on target left untreated.
IPv6 addressing has upgraded DHCP to DHCPv6, which is believed to be more stable and secure.