FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
FQDN, short for Fully Qualified Domain Name, is a complete address of the computer, server, website, and all that are part of the Internet.
Its full name defines location, purpose, and significance on the Internet.
What is a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)?
A Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is the absolute domain name given to a host or a computer on the Internet.
The “Qualified” here indicate the “specified” name that describes the domain name’s full location.
And, if a domain name is not “fully specified,” it is a partially specified domain name (PSDN).
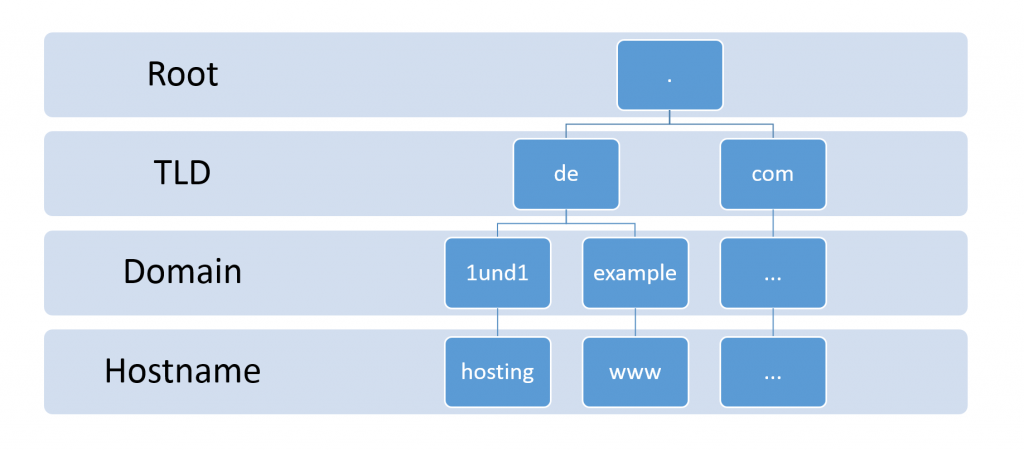
It specifies the hostname, second-level domain name, and top-level domain name (TLD) separated by a period and ended with a trailing period.
For instance, “www.google.com.” is the Fully Qualified Domain Name.
In this example, “www” is the hostname, “google” is the second-level domain name, and “com” is the top-level domain name. In the last, there is a “trailing period,” which signifies the end of the address or path.
Usually, we don’t see the period in the end or add it while writing the website address. The web browser resolves the web address on behalf of us by adding a trailing period.
If we put the whole thing in syntax, it looks as below.
[Hostname].[Domain name].[TLD].
But, if you have a sub-domain name, then you can modify the above syntax as
[Hostname].[Sub-Domain name].[Domain name].[TLD].
Remember, sub-domain is not the hostname. So, the example of the above syntax is
“www.drive.google.com”
Further, the hostname can change with the purpose of the specific service or protocol.
Similar to the “www” hostname, there is hostname like “mail” or “FTP.” Moreover, the Fully Qualified Domain Name indicates the object’s exact location inside the DNS hierarchy.
What is a Partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN)?
A partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN) is just part of the complete domain.
In the previous example, google.com is the Partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN) without the host “www.”
In other words, PQDN can define one or two labels from an FQDN.
It means that google.com can be the one label from an FQDN, and drive.google.com can be another label from an FQDN.
Similarly, digitalmediaglobe.com is the Partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN), and www.digitalmediaglobe.com is the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
Moreover, a Partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN) is helpful for website visitors or users who like to have a simple way to reach a website.
Further, it is the work of the web developer and web browser to put a code so that it will redirect to a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
What is the purpose of a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)?
A Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is required to remove the ambiguity with domain entries.
The web browser with a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) can understand each piece of information accurately and locate the destination.
You can understand Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) as similar to fully qualified PC-DOS that require a command line.
The command line in DOS locates the file or folder in your personal computer’s hierarchical data storage system.
Moreover, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) has defined the specific resolution process for Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
This way helps establish consistent and uninterrupted communication between two hosts.
Why do you need a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)?
The Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is required to access the Internet by configuring your DNS and IP address.
It is also required to configure an SSL certificate, recommended to every website for encrypted communication.
Furthermore, a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is helpful in remote access. The DNS server resolves the FQDN to the corresponding IP address by performing a DNS lookup.
Additionally, a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is accessing a protocol or service such as FTP or Mail.
Conclusion
We all use a fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) without knowing its significance.
However, FQDN and PQDN are not the same. FQDN defines the hostname plus domain name absolute path, whereas PQDN defines the small portion or relative domain name of the FQDN.