FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
DNS Namespace is the space of all names in the Domain Name System. It is very similar to the IP address space, consisting of all possible IP addresses in a network.
Moreover, IP address space is divided into IP address classes like Class A, Class, B, etc. This similar type of division can also be seen in DNS Namespace.
The DNS Namespace is one of the main components of the Domain Name System (DNS). The other two components of the Domain Name System (DNS) include DNS Nameservers and DNS resolvers.
The DNS namespace is also referred to as a namespace or domain namespace. The DNS namespace is a name service provided by the Internet, helping in Transmission Control protocols networks/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
So, how to define DNS Namespace?
Definition of DNS Namespace and its hierarchy
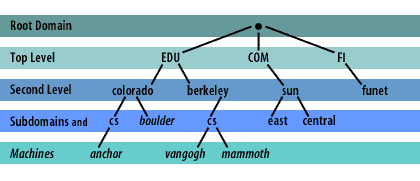
DNS Namespace is the hierarchical inverted tree-like structure that contains a collection of DNS administrative domains all over the world.
From the above Namespace hierarchy, we can depict that DNS Namespace consists of domain and subdomain relative to each other.
It means that a domain can be a subdomain to the domain above it and a parent domain for the hierarchical level domains.
DNS Namespace Levels
The hierarchical inverted tree-like structure consists of the following parts:
- Root domain
- Top-Level Domain (TLD)
- Second Level Domain
- Sub Domain
The topmost part of the inverted tree structure is called the Root. The Root marks the beginning of the structure and is denoted as the dot (.)
Followed by Root, there are Top Level Domains (TLDs). The most common Top Level Domains are .com, .net, .gov, .org, .edu, etc.
It is controlled by an organization ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers), and its subsidiary organization, IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority).
The Second Level Domain, which comes after TLD, is used and registered by an individual or organization.
For instance, digitalmediaglobe.com is the Second Level Domain.
The IANA assigns the Second Level Domain (Internet Assigned Number Authority).
After the Second Level Domain, an associated subdomain can be controlled by the domain owner.
Overall, DNS Namespace identifies and depicts the structure of the domains that can be combined to form a complete domain name.
A complete domain of a host starts from the Root and ends up in a domain or subdomain, where each level is separated by period (.) known as Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).
For instance, “support.digitalmediaglobe.com.” is the Fully Qualified Domain (FQDN).
Here, the trailing period (.), which ends up in the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), is usually omitted at the DNS query.
The domain name points to an IP address (IPv4 or IPv6), which is resolved by a DNS resolver.
The DNS resolver goes through the DNS records, which are then retrieved from the DNS Nameserver.
For a complete understanding of DNS, you can follow this guide.