FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
You would have got confused when you hear these words: public and private IP addresses.
It is important to know the differences between public and private IP addresses.
It also makes you aware which IP address is exposed to the internet and which IP address must establish internal communication.
The public IP address is known as a global or external IP address since it interacts with many networks and is sometimes also referred to as WAN addresses.
The private IP address is used for internal purposes, known as an internal or local address. Moreover, it is used only in the local network.
If you don’t know your public and private IP address, you can follow this guide.
Public IP address
What is a public IP address?
A public IP address is an address assigned to a device when connected to the internet.
Moreover, to connect with the internet, every device on the internet must have a unique IP address.
A unique IP address will be able to distinguish one device from another device.
The public IP address can be assigned to a personal computer, web server, or an email server.
Who assigns public IP address?
Internet Standard Groups assign public IP addresses.
The internet standard groups are the Network Information Center (NIC) or the Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA), which decides the block of IP addresses be distributed.
The block of IP addresses can be distributed to Internet Service Providers (ISP) or large organizations.
The internet service providers (ISP) again distribute the IP address to their users(customers).
What is the scope of a Public IP address?
As discussed earlier, the public IP address is primarily used to access the internet.
With the internet, you can access any device and send data from one computer to another computer.
Access multiple websites and send files
The internet helps you to surf many websites which are located on different servers of the world.
You can also be able to access your files from the Cloud or can send files to a different server using FTP (File transfer protocol).
Organize your own server
The public IP address helps you organize your own server for different purposes such as VPN, FTP, websites, etc.
The home server can assist you in publishing content on the internet using protocols like HTTP.
You can also set up your own VPN using a protocol like PPTP/IPSec/OpenVPN.
You can do other things like set up media (audio/video) server, game server, etc.
Access from anywhere
The public IP address helps you to access your own computer remotely from different places.
It will help you set up a video surveillance camera, and you can access it from any part of the world.
How many public IP addresses assigned in a home network?
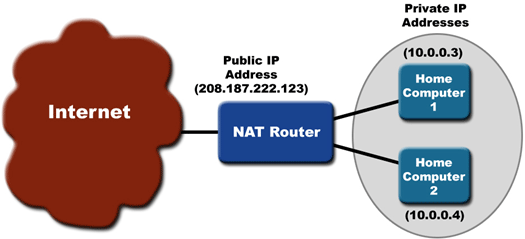
In a NAT-enabled IPv4 router, you can have one public IP address for your home network.
In this case, the router is the center of communication between your computer and the internet. So, the router has been assigned with one public IP address.
It doesn’t matter how many devices are connected to the router. Further, in this article, we will discuss how NAT helps to communicate on the internet.
What are the public IP addresses ranges in general?
The actual public IP addresses ranges as below:
| Class | Public IP Ranges |
|---|---|
| Class A | 1.0.0.0 to 9.255.255.255 11.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255 |
| Class B | 128.0.0.0 to 171.255.255.255 173.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 |
| Class C | 192.0.0.0 to 195.255.255.255 197.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 |
| Class D | 224.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255 Multicast Addresses |
| Class E | 248.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254 Experimental Use |
The public IP address is issued by an Internet service provider (ISP), and the range of IP addresses generally varies from 1 to 191 in the first octet of the IP address.
But, there is some exception, where some IP address blocks are reserved for private address ranges.
It starts at 10.0.0 for the private network in class A, and in-class B, it starts at 172.16.0.0 for the private network.
Most of the LAN network uses “Class C” as a private IP address. That’s why most of the home or office network has private IP addresses starting from 192.168.0.0.
The most common LAN IP addressing scheme is from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.254, where the first three octets remain the same, and the last octet changes with the number of devices.
You can follow this guide to know more about IP address classes.
Private IP address
What is a Private IP address?
A private IP address is an address assigned to a device in an internal network or LAN and cannot be used to route your internal activity on the internet.
It means that you cannot send any data outside of the internal network or on the internet.
The private IP address is used to communicate with a device within a network.
Who assigns a private IP address?
InterNIC allocates the private IP address to an organization or ISP.
The InterNIC is an organization that provides internet information and domain name registration services.
It allows an organization or ISP to create their own private network.
Also, the InterNIC is run by the Internet Corporation For Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
Which devices are assigned with a private IP address?
Any device that resides in a local network or home network or the network within an organization is assigned with a private IP address.
The devices can be a computer, smartphones, tablets, printers, etc.
Within a network, the devices can communicate with a private IP address.
But, outside the network, you cannot communicate with a private IP address.
Moreover, the private IP address can be the same for two different networks.
Additionally, the automatic assignment of private address in an internal network is done through a DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) from your router.
What are private IP addresses assigned to a network?
The following private IP address ranges that belong to IPv4 Classes A, B, and C are listed with a subnet mask.
- For Class A – The IP address ranges from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 or /8 (8-bits belongs to network ID).
- In Class B – The IP address ranges from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 with a subnet mask of 255.240.0.0 or /12 (12-bits belongs to network ID).
- For Class C – The IP address ranges from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 or /16 (16-bits assigned to network ID).
- Special IP address – The IP address ranges from 100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255 with a subnet mask of 255.192.0.0 or /10 (10-bits assigned to network ID).
For a clear understanding, you can refer to our guide on IP address classes, subnet, and subnetting, and for CIDR notation (/8, /16, /24), you can refer to this guide.
Moreover, the above-listed IP address is known as the reserved IP address intended to be used only in the internal network.
The reserved IP address cannot be controlled outside of the internal network, and it has no direct access to the internet.
How to communicate on the Internet with a Private IP address?
As we have discussed, the private IP address is used in the internal network only.
You cannot communicate on the internet with a private IP address.
To solve this problem, the NAT (Network Address Translation) is introduced.
NAT is a process in which a private IP address is replaced with a public IP address to communicate on the internet.
When you send any data over the internet, it replaces your private IP address with the public IP address and forwards it to the destination.
Similarly, when you receive traffic, it will first replace the public IP address with your private IP address and forward it to your computer.
The private IP address is strictly for your internal network or the network within an organization and for the router connected to that network.
Moreover, the private IP address will also remain hidden when you are connected to the internet. The IP address that is visible to the other end of the network is the public IP address.
Public and Private IP address analogy
We can define and differentiate public and private IP addresses using the zip code analogy.
A public address is similar to a zip code, which defines the area you are located in.
But, in an area, there could be many apartments.
Here, the apartment is your private IP address.
When a mail is sent to your zip code (public IP address), it first reaches the main post office (DHCP).
The main post office (DHCP) is further distributed to the local post office or area post office (router).
The local post office (router), with the assistance of the main post office (DHCP), will reach your apartment (private IP address).
We hope the above analogy helps you understand the concept and functionality to some extent.
Takeaway
Private IP addresses are always intended to use in the local area network. Moreover, it cannot be accessed outside the network.
A public IP address is used to communicate throughout the internet. It is basically assigned by the ISP (Internet Service Provider).
The public IP address can easily be found using the online tools, whereas the private IP address can be detected using the command prompt.
Also, the private IP addresses are assigned randomly using the DHCP protocol.
With a private IP address, you can interact only with internal network devices and the router through which you are connected.
If you intend to connect to the internet through a private IP address, it can be achieved via NAT (Network Address Translation).
The work of a NAT is to replace a private IP address with a public address.