FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
Circuit switching and packet switching are two different switching methods in networking technologies. Switching determines the path and connection between multiple network devices connected.
In networking, the devices in a network are connected using software and hardware that allows for exchanging information.
Moreover, there are different methods for the exchange of information that take place between networking devices.
Further, the different method for exchange of information is categorized and described. Also, which type of networks can be used with these methods.
The fundamental way of differentiating networking technologies is to determine the path it takes to flow between connected devices.
In highly simplified terms, you can determine using two basic approaches:
- In advance, a path can be set up between two devices in a network
- Let individual data elements decide the best possible path over a variable path.
Basically, there are two methods of switching:
- Circuit switching
- Packet switching
Both techniques are used in switching with basic differences in working and connection.
Circuit Switching
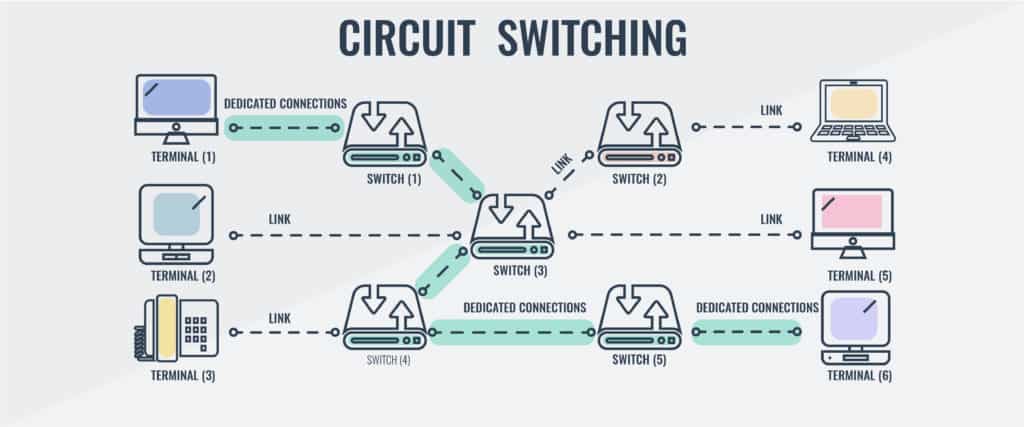
In a circuit switching, the connection is called a circuit, which takes place between two devices in a network.
Further, the whole communication using circuit switching depends on the nature of the circuit in a network.
The circuit can be fixed, which means it will always be present between two devices or create the circuit on an as-needed basis.
Moreover, there would be multiple possible paths through intermediate devices, but it can be used only on one path for a given dialog.
From the above illustration, you can see there is a dedicated connection between the two devices. There are multiple paths, but only one path is set up and dedicated for communication.
To understand circuit switching, the best and classic example is the telephone system.
In a telephone system, when you call someone, and they answer, you have established a circuit connection, and now you can pass data stream to this circuit.
Moreover, the flow of information would be the same regardless of how many intermediate devices are used in a circuit connection.
The established circuit you can use as long you want and then terminate the circuit after use.
Further, when you call again, it will establish a new circuit, and most probably, new hardware would be available to complete the circuit.
Packet Switching
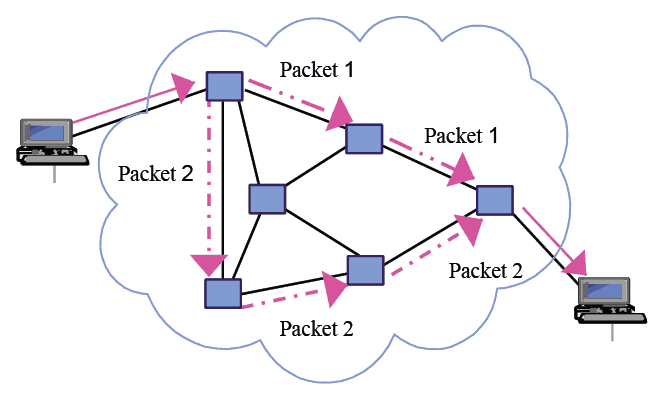
There is no need to establish a specific path or dedicated path to transfer data in packet switching.
The data is not sent at once; instead, it is divided into small blocks called packets and then sent to the network.
Moreover, the packets can have their own separate and discrete path, which depends upon the availability of the shortest and quickest path at the time of transfer.
Further, the packets are routed, combined, or fragmented to reach the eventual destination.
Conversely, at the receiving end, the packets are read and re-assembled to form original data.
Packet switching is more similar to the concept of the postal system than the telephone system.
In the above illustration, we can observe no circuit is set up before sending data between devices.
Further, the data is broken into blocks called packets, and each packet has taken a separate path to reach the destination.
Circuit switching and packet switching: which is better?
Well, it depends!
There would be the case when one is superior or suited best than the other.
Also, the selection of switching methods depends on whether the network is shared or dedicated.
In a telephone system, circuit switching is established where it follows the dedicated path, and only one can use it at a time.
This will not fit well in the LANs (Local Area Networks) system, where multiple devices share the medium. In such cases, packet switching is more suitable.
In today’s networking, packet switching is predominantly preferred over circuit switching because it allows multiple devices to communicate simultaneously without a dedicated path.
Moreover, there would be the possibility of packet loss during transit in packet switching. Though it does not matter in some situations, it will greatly impact a different type of communication.
Difference between circuit switching and packet switching
Differ in technology
Circuit switching is connection-oriented, establishing a dedicated connection between two or more devices before sending data.
Packet switching is connectionless, which means there is no need to establish a connection for transferring the data over a network.
Number of connection and path
Circuit switching can have a single dedicated connection at a time between two devices in a network. Also, it will follow a uniform path throughout the session.
Packet switching can have multiple connections simultaneously, but there is no uniform specified path from end to end session.
Performance and efficiency
Circuit switching is preferable for voice communication because it provides consistent bandwidth, channels, and data rate in terms of performance.
Also, circuit switching gives surety that the delivery of the data packets is in the correct sequence.
Packet switching is preferable for data transmission because of its efficiency.
The data packets will quickly determine the path needed for the destination without the requirement of a dedicated channel.
Moreover, if there is a packet loss or failed delivery, it will resent the packet.
Cost-effectiveness
Circuit switching requires a dedicated channel for a single service which makes it unavailable for other services.
This factor makes circuit switching expensive for dedicating an entire channel for a single service.
Also, with the increased number of active users, channels won’t be available for all users, making calls fail or drop.
Packet switching doesn’t require a dedicated channel for data transfer, reducing the cost incurred to maintain the entire network.
Conclusion
Overall, packet switching is more efficient and cost-effective compared to circuit switching.
But, the circuit switching technique is more efficient for voice transmission than packet switching.