FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
You have heard of the router so many times but not often heard of the wireless access point.
Is wireless access point and router the SAME thing? Absolutely not!
Here, we will discuss and distinguish how the wireless access point and the wireless router differ?
Also, when you need a wireless access point and wireless router in a network?
What is a router?
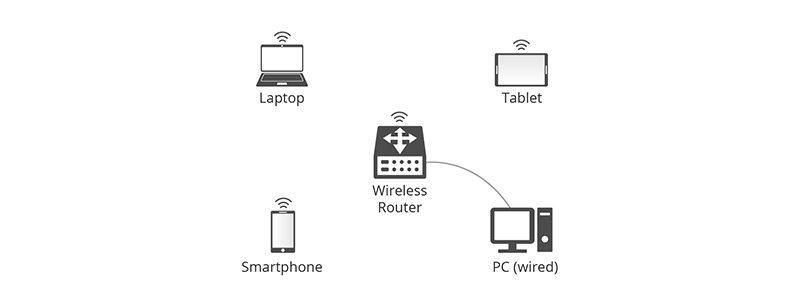
A router is a network device that connects all your devices in a local area network (LAN) to the modem or gateway through Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
Further, router functionality is to transfer and distributes data from the internet to the connected devices.
Deployment of the router can establish a local area network (LAN) and allow each device in a network to interact with each other.
Concisely, when your modem or gateway receives information from the internet, it transfers it to the router. The router further transfers it to the device or computer, who asked for it.
Additionally, the network created by your router is known as a local area network (LAN), and the network through which it is connected or collecting information – mostly, the internet – is known as a wide area network (WAN).
Wired router
Traditionally, the router was connected to the LAN (Local Area Network) devices through an Ethernet cable known as wired networking.
The wired router has its own drawback. You can not connect too many devices with a wired router.
Also, it required an ethernet wire to connect to the devices so that you can extend it to a longer distance.
Wireless router
Over time, with a wireless router, you can now connect multiple devices in the LAN wirelessly.
It is considered as user-friendly and suitable for many homes and small offices.
Moreover, the wireless router is suitable for only Wi-Fi-enabled devices like laptops, tablets, smartphones.
Additionally, enterprise wireless routers can be used for Voice over IP (VoIP) calls and support IPTV or digital TV services.
The router can also have firewall and password protection functionality that protects you from threats outside LAN.
What is an Access Point?
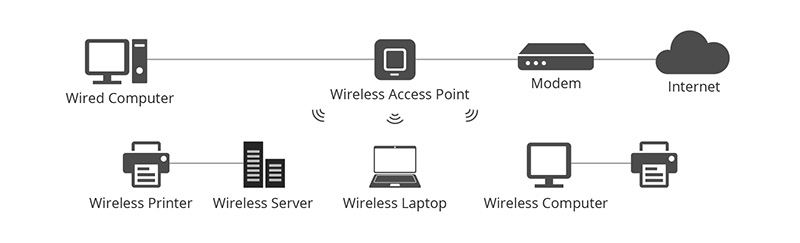
An access point is a wireless network device, which is also known as Wireless AP or WAP.
Wireless access points act as a portal that adds Wi-Fi capability to the existing LAN network by bridging traffic from the router or gateway into the LAN network.
Additionally, the wireless access point can act as a stand-alone device with an in-build router or a router component.
The wireless access point can be used in two cases:
Firstly, the wireless access point can assist the existing wireless router in reaching out to devices that don’t have an inbuilt Wi-Fi connection. It will then connect to these wired devices through an Ethernet cable.
Secondly, the wireless access point can extend the wireless coverage of the existing wireless router to connect more devices at a longer distance.
Difference between Wireless Access Point and Router
Wireless access points and router both seem to be similar because both support Wi-Fi network connectivity. But, they differ in functionality and connectivity.
Differ in Functionality
In general, the router covers the functionality and plays a role of the wireless access point, an Ethernet router, firewall, and Ethernet switch.
But, wireless access point devices can have inbuilt router or Wi-Fi network extenders compatibility.
In other words, all routers can behave as a wireless access point, but not all wireless access points can work as a router.
Moreover, the wireless router can play the Ethernet hub’s role in establishing the local area network (LAN) by linking and managing all the devices connected to it.
Additionally, the wireless router can be used to change the network settings, but the wireless access point is not equipped with this functionality.
Differ in Connectivity
The router and wireless access point both differ in connection.
The router can provide Wi-Fi signals to the LAN devices directly, or you can extend the Wi-Fi coverage by connecting the wireless access point using a PoE switch.
The wireless access point which doesn’t have routing functionality needs a Wi-Fi router as an intermediary to connect to the gateway or modem.
Extend wireless coverage
The wireless router is typically for a home network or small offices. The coverage area of a router can be limited to a certain area.
So, if your device falls outside the coverage area or lies in dead spots, then it cannot get Wi-Fi signals.
In such conditions, the wireless access point helps extend the wireless coverage area, eliminates dead spots, and can accommodate more devices.
Keep up future demands.
In-home network or small offices, a wireless router can meet up the demands of the users, which is mostly limited or fixed.
But, in large organizations or enterprises, the demand grows with the increasing number of users.
So, for medium to large enterprises or organizations, you will need one or more wireless access points to involve multiple users.
Unlike previous cases, the network manager can add additional access points to meet the growing demand of many users.
The wireless access point is also effective in maintaining a higher-performance and reliable wireless network.
Conclusion
Wireless router vs. wireless access point differences will depend on your needs.
Before considering a wireless router or wireless access point, you need to examine some of the factors:
- The coverage area of the current network and the demand to extend the coverage area.
- The current number of Wi-Fi users and the demand to increase the number of users in the future.
The wireless access point has allowed large enterprises to extend the existing LANs.