FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
You would have heard of virtualization many times when dealing with cloud computing. But, the concept of virtualization is not understood correctly and how virtualization plays a crucial role in utilizing the available resources.
There are many types of virtualization, and the most common are desktop virtualization, network virtualization, cloud virtualization, and storage virtualization.
The main advantage of using virtualization is resource efficiency.
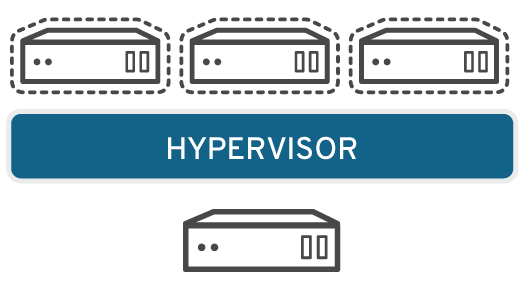
Suppose you have three physical servers, and each server is dedicated to a particular task like a mail server, web server, and running legacy application.
But, all three physical servers are not appropriately utilized. It uses only 30% of the overall resources. So, when we introduce virtualization, we can include all three tasks in a single server by providing dedicated resources to each task.
In this way, by using virtualization, we can have less maintenance and running costs. Apart from this, the resources are adequately utilized.
Let’s look into the more profound aspect of what virtualization is and how does it work.
What is virtualization?
Virtualization is creating and running virtual instances of a computer system in a layer abstracted over computer hardware.
The hardware elements of a computer system are processors, memory, storage, and more, which is divided into multiple virtual instances called a virtual machine (VM).
Moreover, the Virtual Machine runs independently and has a dedicated virtual operating system.
However, there could be multiple virtual machines, and each virtual machine is just a small portion of the actual underlying computer hardware.
In order words, we could say that the virtualization concept allows proper utilization of computer hardware. It further helps you to get a better return on your investment.
Also, virtualization provides you a scope to scale your computer hardware when needed.
How does virtualization work?
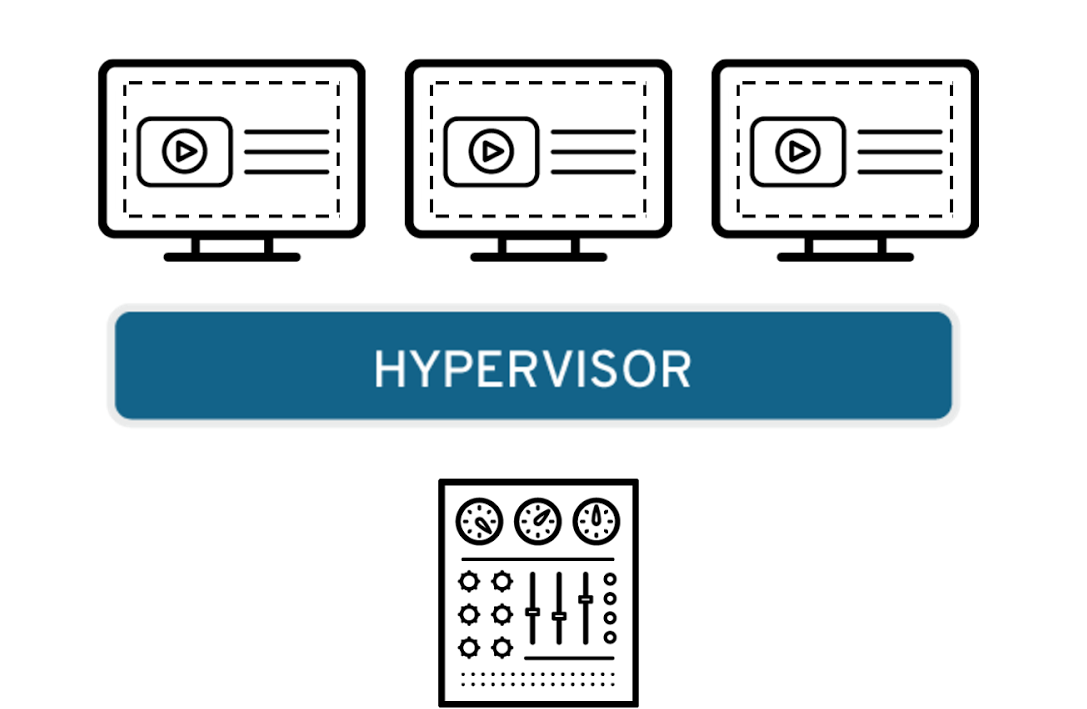
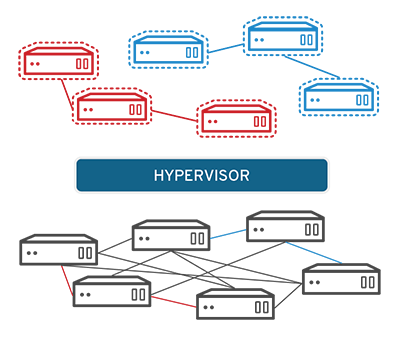
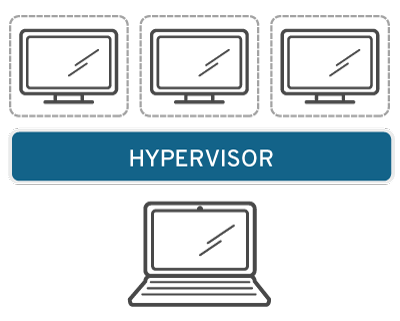
Virtualization takes place using software like hypervisors which separate the physical resources and virtual environment.
The physical resources can be OS, storage, or any other hardware equipment installed and connected with the computer or server.
Moreover, the virtual environment contains multiple virtual machines that work as separate entities and have their own resources abstracted from physical resources.
However, physical resources are partitioned to cater to multiple virtual machine requirements.
Also, when the user or program requests additional resources, the virtual machine conveys the message to the virtual environment. Further, the virtual environment puts a request to the physical system and caches the changes.
Hypervisors are Type 1 Hypervisors (Bare Metal) and Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted).
Type 1 Hypervisors installed over physical machines make it most popular, secure, and lower latency.
Typical examples of Type 1 Hypervisors are VMware ESXi, Kernel-based VMs (KBV), and Microsoft Hyper-V.
Type 2 Hypervisors are installed over a layer of host OS between Hypervisor and virtual machine.
Moreover, Type 2 Hypervisors are mainly used for end-user virtualization, including Oracle VirtualBox or VMware Workstation.
Benefits of virtualization
Utilization of Resources efficiently.
Before virtualization, each legacy application requires a separate server to run. It means that you have to separate dedicated CPUs for each application.
Invariably, physical servers are not utilized fully or remain unused. In contrast, the virtualization of a physical server lets you run multiple applications on its separate virtual machine, each provided with a dedicated OS.
Further, virtualization never compromises your reliability, nor does it let your physical server remain unused.
Easy to manage
Before virtualization, it was challenging to maintain a separate physical server for each application and workflow. But, when the physical server is changed to a software-based virtual machine, it efficiently manages multiple virtual machines on a single physical server.
Also, you can create management policies for each virtual server, which further let you create automated IT service management workflows.
The automation tools based on services help you to deploy services repeatedly and consistently. In addition, this doesn’t require any manual setup, and also, the automated configuration can be implemented error-free and in less time.
Moreover, you can also deploy different security measures and configurations based on the role of the virtual machine.
Furthermore, you can increase resource efficiency quickly by retiring unused virtual machines.
Minimize downtime
Downtime occurs when OS or application crashes, which in turn disrupt user productivity. With virtualization, you can have multiple redundant virtual machines, which can be used as a backup in case of any failure.
So, when there is a crash on one virtual machine, it will switch to another virtual machine with the same setup. This process is called failover, where it automatically switches to the backup system.
In the same process, if we apply on the physical server, we need to have multiple physical servers, which could be highly expensive.
Type of virtualization
There are many types of virtualization, but the most common is server virtualization. However, most of the IT infrastructure elements can be virtualized to take advantage as a whole.
In this section, we will discuss a different type of virtualization.
Desktop virtualization
Desktop virtualization is the process of creating a virtual machine that can run its own operating system.
Further, you can have two types of desktop virtualization, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) and local desktop virtualization.
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) runs virtual desktop on a virtual machine created on a central server. Later, it gives access to users who can log in from their client devices.
Local desktop virtualization uses software like Hypervisor to create a virtual machine that can run multiple local desktops on your local computer. It is helpful to users who like to experience multiple OS installed in multiple virtual machines without switching to another computer.
Network Virtualization
Network virtualization is the process of creating multiple instances of a network on a single console. It will abstract hardware elements and functions into software running on Hypervisor.
Moreover, the hardware element and function could be switches, routers, or connections. Further, the modification and control of these hardware elements and functions make network administrators easier without touching the underlying physical components.
The two most common types of network virtualization are software-defined networking (SDM) and network function virtualization (NFV).
Further, the Software-defined networking (SDM) virtualizes hardware that controls network routing and traffic. At the same time, network function virtualization virtualizes one or more hardware appliances that provide a specific function to networks such as firewall, traffic analyzer, or load balancer.
Storage Virtualization
Storage Virtualization combines all storage devices in a network to be accessed and managed as a single storage device.
And, the storage device that is combined in a network can be installed on a single server, or it can be standalone storage units.
Further, the block of storage can be assigned to the virtual machine as needed. The storage virtualization usage is seen on Cloud storage.
Data virtualization
Data virtualization is one of the practical, affordable, and feasible ways to access data from the remote location of any format through multiple applications.
Moreover, data virtualization act as an accessing layer between application, who would like to access data and the system storing the data.
The storage of data can range from the cloud to in-house storage hardware systems. And it can be located in multiple locations.
So, when the software layer, created by data virtualization tools, receives a query from multiple applications, it returns storage systems.
Application virtualization
Application virtualization is a way to run applications on the user end without installing them directly to the user’s OS.
It is a way to give access to some part of the application to run in a virtual environment.
There are mainly three types of application virtualization
Local Application Virtualization – In this case, the entire application is installed in native hardware but runs on the endpoint device.
Application streaming – The application lives on a server, but it gives access to small software components to run on the end user’s device.
Server-based application virtualization – The application is installed and runs entirely on a server, and it only gives access to the user interface to the end-user.
Datacenter virtualization
Datacenter virtualization is a process of enabling multiple physical data centers into virtual data centers.
The software-based virtual data center presents the data center environment to the user without purchasing underlying infrastructure hardware.
CPU virtualization
CPU virtualization divides a single CPU into multiple virtual CPUs for use on numerous virtual machines.
It uses software-based technology to have a virtual CPU which in turn improves virtual machine performance.
GPU virtualization
GPU virtualization is a process that lets the virtual machine use all or some part of the single GPU processing power to improve VM performance.
A graphical processing unit (GPU) is a multi-core processor that improves the performance of heavy graphics for faster video, artificial intelligence, and applications.
Moreover, the GPU virtualization can be two types: pass-through GPUs that make the entire GPU to a single OS on a virtual server.
And Shared vGPUs divide single GPU cores into multiple virtual GPUs for use in virtual servers.
Linux virtualization
Linux virtualization involves kernel-based virtual machine (KVM), same as Hypervisor.
It supports Intel and AMD’s virtualization processor to create x86-based virtual machines hosted on Linux OS.
Moreover, Linux virtualization is highly customizable that can be used for specific workloads and applications.
Cloud virtualization
Cloud computing involves cloud virtualization, which is processed by virtualizing servers, storage units, and physical data centers.
Moreover, cloud computing provides an extensive range of services which includes Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), Platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).