FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
Topologies are the basic building blocks of networks. A network topology is the arrangement of nodes within a network and the links between them.
In a computer network, the network’s topology refers to the layout of the nodes and their connections. There are a number of different topologies that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
This article provides an overview of the most common types of network topologies, including peer-to-peer networks, hierarchical networks, ring networks, and bus networks.
What are Network Topologies?
Networks can be classified by their topology, which refers to the physical layout of the nodes and communication links.
Different networks have different topologies, but all networks have nodes and a communication medium.
Moreover, different types of networks are designed to achieve different goals. Topology helps network administrators allocate resources efficiently and ensure the network’s health.
A proper network topology makes it easy to restructure and rearrange nodes. It also increases data efficiency while reducing maintenance and operational costs.
However, network topologies are not universal and can vary from one network to the next.
Understanding network topology is important for understanding how data is transferred and processed in a network.
Types of network topology
There are several different types of network topology. Each one has its pros and cons. Choosing one over another can be tricky.
When choosing a network topology, scalability, reliability, and budget are a few things to consider.
There are five main network topologies: bus, ring, star, mesh, and tree. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Star, bus, and ring topologies are the most common types of network topologies.
However, if your network is big or complex, you may want to consider other options. Choosing the correct network topology depends largely on your budget.
More complex arrangements require more cable and are more labor-intensive. However, they are more durable and easier to manage. For this reason, star topologies are preferred by many.
A tree topology combines the features of star and linear bus topologies. It divides a large network into manageable parts linked through a central hub.
However, this network is highly dependent on this central hub, which can fail. Therefore, a failure in one part can cripple the whole network.
As a result, it is important to select the right network topology before choosing one. Once you know the basic types of network topologies, you can design a network that works for you.
Read on to find out more! Here’s an overview of the most popular types of topology. Consider their pros and cons and choose the one that works best for your needs.
Bus Topology (Advantages and Disadvantages)
A bus topology is a network topology in which each node is connected to a single cable. Data travels from one node to the next until it reaches its destination.
This type of topology is simple and easy to set up, but it can be difficult to troubleshoot when there is a problem.
Advantages of Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a common cable. This type of network is very simple to set up and is often used in small networks.
One of the advantages of bus topology is its ease of installation. This type of network configuration does not require any external device, including routers or switches, and is easy to manage.
However, it is limited in size and can be complicated to troubleshoot if any one device becomes unresponsive.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
The biggest disadvantage of a bus topology is that if one device fails, the entire network will fail.
Additionally, the bandwidth available on a bus topology is limited to the bandwidth of the cable.
This topology is best suited for small networks, as it requires only a single backbone cable and can be extended or decreased without affecting other devices in the network.
Another disadvantage of bus topology is that it increases the risk of network failure. Because each device is linked to another through a single backbone, any damage to the backbone can cause the entire network to crash or split.
The backbone is also limited in length, so the number of computers and peripherals will be limited. The risk of collisions increases as more devices are added.
Star Topology (Advantages and Disadvantages)
A star network topology is one in which all devices are connected to a central device. The central device, often called a hub, provides a connection point for all other devices on the network.
This type of topology is very common in small networks, such as home networks.
In a star network topology, each device is typically connected to the hub with a single cable. If the central device fails, the entire network will fail.
Many star networks use redundancy to prevent this from happening, meaning they have multiple central devices and/or backup cables.
Advantages of Star Topology
Star Topology is a common network topology with several advantages over other types. For instance, it requires fewer cables than other topologies and is easier to install and manage.
Another advantage of star topology is that it is easy to add or remove devices from the network.
Star networks are also less prone to congestion than other topologies, as data only needs to travel through one device before reaching its destination.
Moreover, it eliminates signal reflection and point-to-point connections.
However, the disadvantages of star topology outweigh the benefits of this network topology.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
Star networks are also more vulnerable to cable breaks or other failures, as the entire network relies on the central device.
The disadvantage of star topology is that if the central device fails, the whole network fails.
In other words, all segments are linked to a central bus. If a single segment is broken, the entire network is down.
On the other hand, a single segment can form a star network with the nodes it serves.
Further, the star topology has several advantages, though physical restrictions limit it.
Although it has a limited number of nodes, it can be extended into a cluster of stars with a central hub at the center.
A star network’s central core acts as the network’s backbone. It is easy to manage but is costly to implement. A star topology can be deployed in a bank network.
Ring Topology (Advantages and Disadvantages)
Ring topology is a type of network topology in which each device is connected to two other devices, forming a loop.
Moreover, Ring topologies are often chosen for small networks because they are simpler to set up than other topologies.
This type of topology is often used in local area networks (LANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs).
Ring topology is relatively simple to set up and can be less expensive than other types of topologies. However, it can be more difficult to troubleshoot than another type of networks and more susceptible to failures.
The Ring Topology is one of the network topologies that use UTP or Patch Cable to connect all the devices in a network.
A ring contains a series of points, each having a transmitter and a receiver. The points form a circle that data packets can pass through either on the left or right side.
Advantages of Ring Topology
The ring topology is a relatively simple topology in which all the nodes are connected in a loop. This makes it ideal for small networks, as it is easy to set up and manage.
Additionally, because there is only one path from any given node to any other node, it is very stable and resistant to failure.
This makes it a good choice for networks that need to be reliable.
The Ring Topology is beneficial for high-speed data transfer and is often used for WAN and LAN networks.
Its benefits include higher reliability and less lag than other network topologies. It also allows for rapid and easy addition of workstations. As a result, it can be an ideal choice for networks with multiple locations.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
There are also some disadvantages to using the ring topology. The first is that it can be inefficient when it comes to bandwidth usage.
A network with multiple nodes will cause communication delays between devices, but a single point can remain active and transmit data without affecting the other nodes.
However, its disadvantages include the fact that it requires expensive hardware components, such as network cards and cables.
Further, there is no built-in redundancy, so if one device fails, the entire network fails.
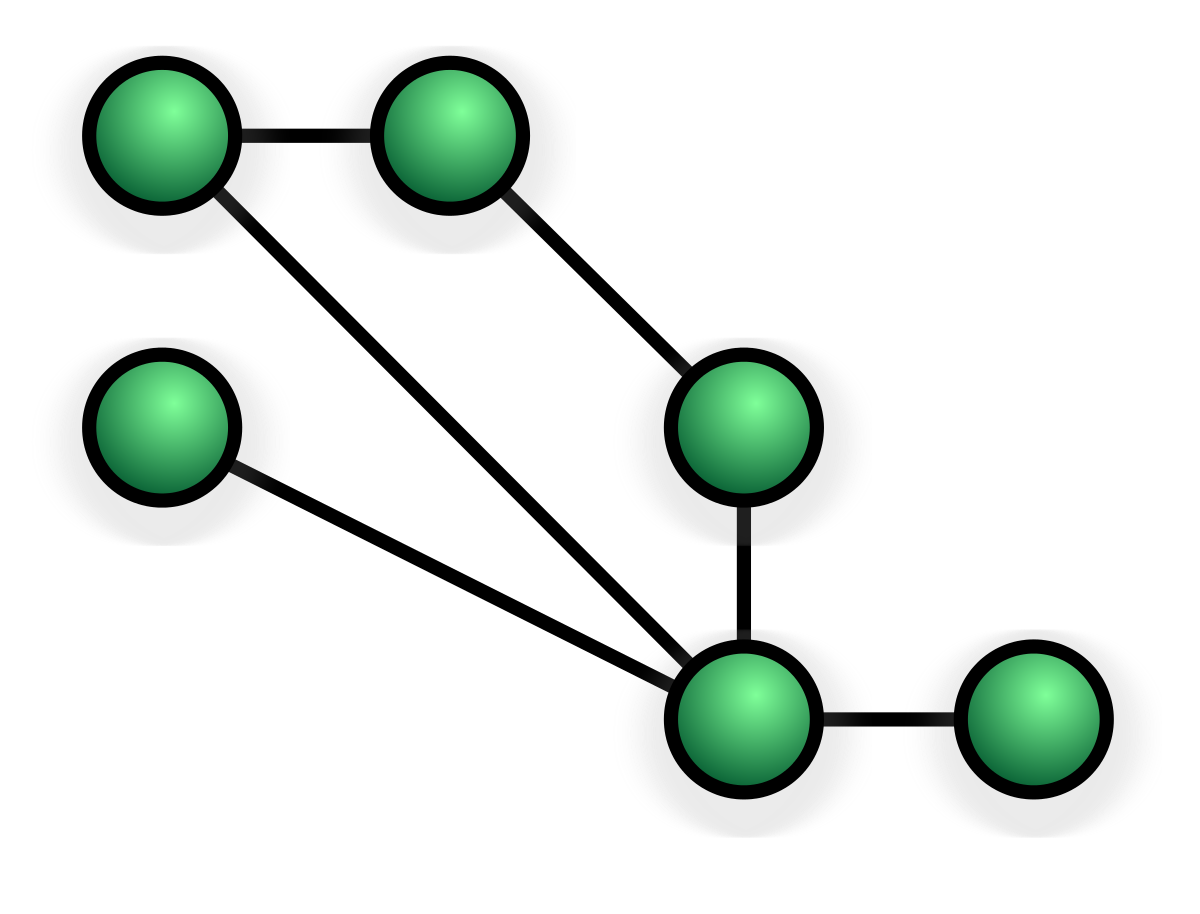
Mesh Topology (Advantages and Disadvantages)
Mesh topology is a network topology in which each node is connected to every other node in the network.
Moreover, Mesh networks are often very reliable because if one node fails, the traffic can be rerouted through the other nodes.
Mesh networks are also suitable for distributing traffic evenly across all of the nodes in the network.
Mesh topology is often used in local area networks (LANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs).
Advantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology has several advantages, including redundant paths and easy addition or removal of nodes.
A significant benefit of mesh topology is its scalability and cost-effectiveness. It is also highly flexible, allowing you to deploy additional nodes wherever you need them quickly.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology also has several disadvantages, including high costs and complexity.
One disadvantage of mesh topology is that it can be expensive to implement. Each additional node added to the network increases the cost of the network.
Additionally, mesh topology can be complex to configure and manage. If a node fails, it can be challenging to determine and repair the failure’s source.
Mesh topology requires a high level of complexity and is often more expensive than other networking options. This is because all nodes must be active, and they have to share their load.
Another disadvantage of mesh topology is its increased power consumption and workload.
As each node must act as both a router and an endpoint, the mesh network tends to have high latency or the time that it takes a message to travel from one node to the next.
Hence, upgrading your mesh network to increase its power, memory, and bandwidth may be necessary to ensure high performance.
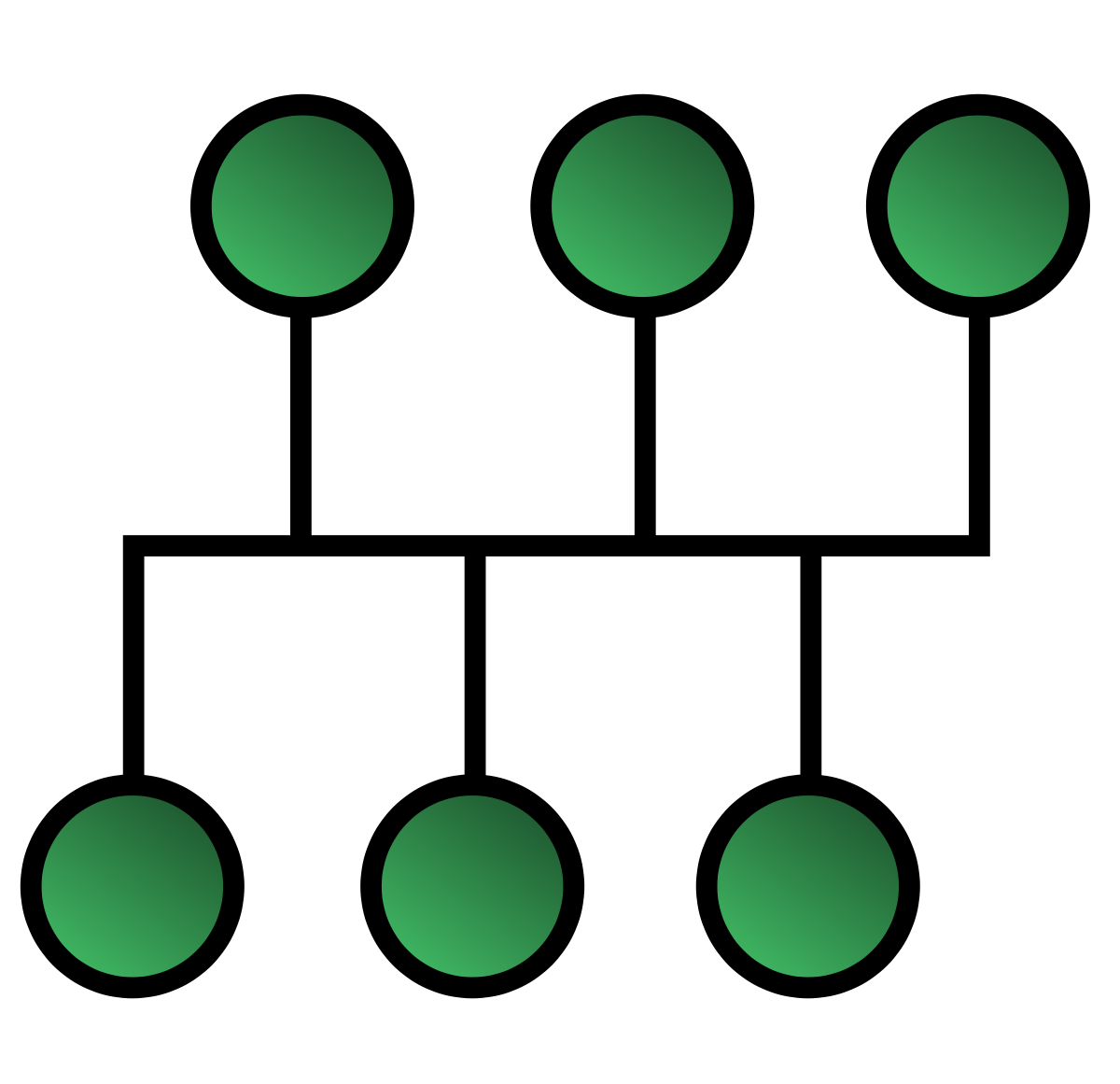
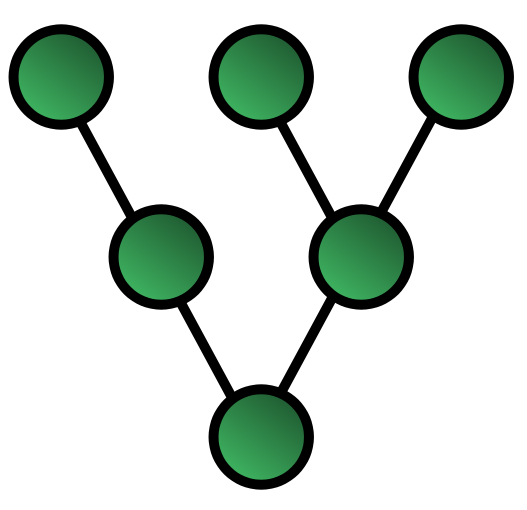
Tree Topology (Advantages and Disadvantages)
A computer network topology is the network nodes’ layout and connections. There are many different topologies, but tree topology is one of the most common.
Each node is connected to two other nodes in a tree topology, called parent and child nodes. The root node is at the top of the tree and has no parent node. All other nodes are branches of the tree, with one final node at the end of each branch.
However, because all communication must go through the root node, it can be slow when large amounts of data need to be transferred.
Tree Topology is a combination of bus topology and star topology. It is useful when networking with multiple departments.
Each department is connected to the central node in this topology, thereby inheriting the advantages of star topology and centralization.
Advantages of Tree Topology
The advantage of a tree topology is that it is easy to understand and visualize. It also has a high degree of redundancy, meaning that the network can still function if one node fails.
The advantage of a tree topology is that it is efficient and easy to manage.
In a tree topology, each node in the network connects to two other nodes, forming a hierarchy. This makes it easy to determine the path between any two nodes in the network.
Tree topology is also efficient because data travels along the shortest path between nodes. This makes the network faster and more reliable.
A tree topology is advantageous when a star or transport topologies cannot be executed independently.
For instance, it’s best suited for systems administration in different universities, enterprises, or college branches. In addition, it’s easier to add secondary nodes and expand them with less space.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
One of the main disadvantages of Tree Topology is its inability to provide a high level of security.
Since the network is organized in a tree, any computer in the network can access data from any other computer in the network.
This means that any hacker that manages to compromise one workstation on the network will have access to all the information on the entire network.
However, it’s also prone to failure. This can make the entire network unusable if the main data trunk cable malfunctions.
One disadvantage of the tree topology is that it can be inefficient when used in large networks. In a large network, messages must travel through many branches before reaching their destination. This can cause delays and increase the amount of traffic on the network.
The main disadvantages of Tree Topology include the need for long cables, which are typically limited in length by default. This can cause wiring difficulties, especially if more than one computer needs to connect to a central hub.
Because of this drawback, tree topology can be difficult to expand or modify.
Furthermore, Tree Topology requires a large amount of configuration time, making it a less desirable network topology for large organizations.
Daisy Chain (Advantages and Disadvantages)
In a computer network, the daisy chain topology is a type of mesh topology in which each node is connected to two other nodes, thus forming a chain.
In other words, a daisy chain topology is a type of computer network topology in which each node is connected to two other nodes; those two nodes are then connected to two other nodes, and so on.
The Internet is one of the largest hybrid networks. The Internet uses Daisy Chain topology, in which each computer is connected to another computer via a network link.
Messages travel up and down the line, eventually reaching the intended computer.
The Daisy Chain topology allows network nodes to be connected in a line or chain. A message is transmitted from one computer to another.
This type of network topology can also be slow and requires more inspections. Moreover, this type of network topology is used in metropolitan area networks.
Advantages of Daisy Chain Topology
The Daisy Chain topology is easier to set up because of its linear nature.
Additionally, daisy chain topologies are less susceptible to network failure because if one node fails, the rest of the network continues to function.
Disadvantages of Daisy Chain Topology
The disadvantage of Daisy Chain is that it is not very resilient to failure, as any breakdown in the chain will cause the whole network to fail.
Although daisy chain topologies can be extended indefinitely, they are unsuitable for long-distance networks.
It requires extensive cabling to connect nodes and is unsuitable for geographically dispersed networks.
It also has a disadvantage in that the cables connected to each node are zig-zagged around the network. This slows down operation at the opposite end of the system.
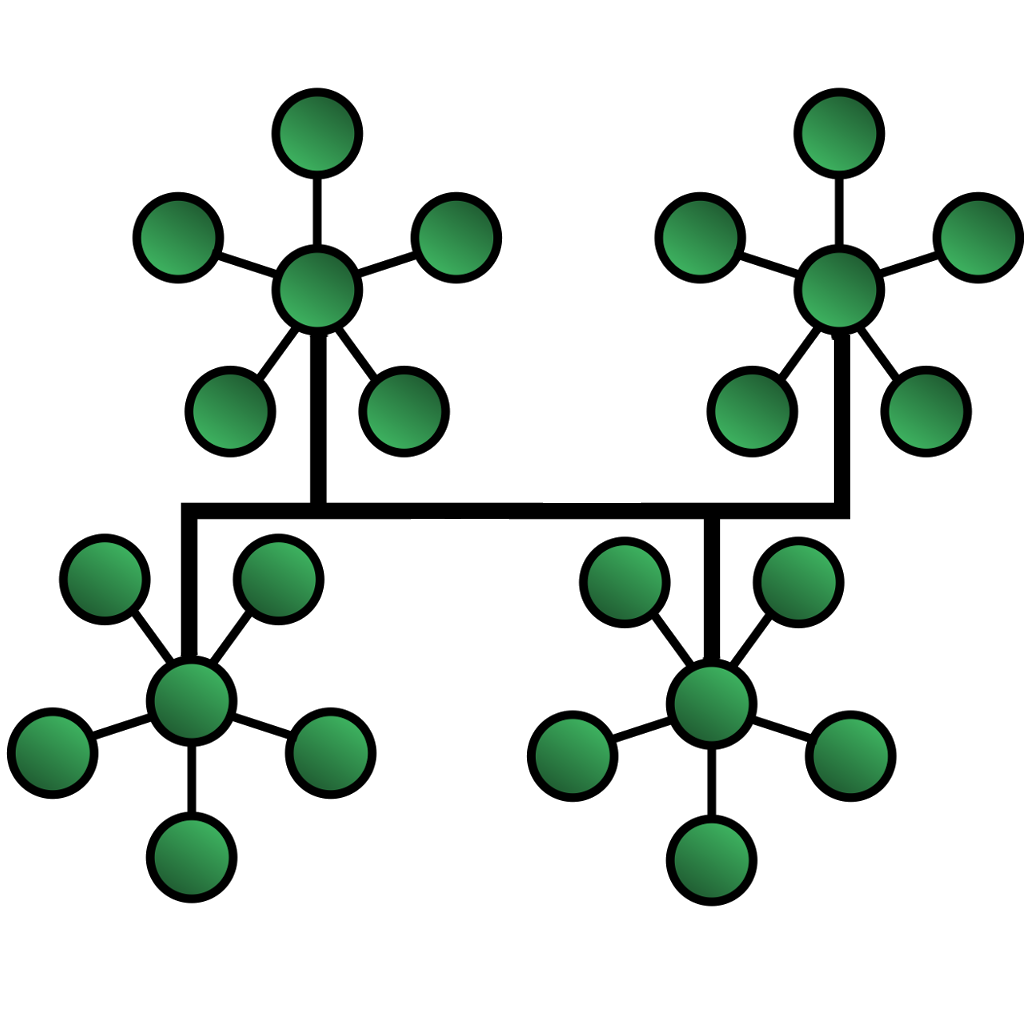
Hybrid Topology (Advantages and Disadvantages)
A hybrid topology is a computer network topology that uses a mix of two or more different topologies.
The most common type of Hybrid topology is the Star-Mesh hybrid topology. In this type of network, some devices act as central hubs (Star), while others connect to them in a mesh fashion (Mesh).
Another example of a Hybrid topology is the Ring-Star hybrid topology. In this type of network, some devices form a ring, while other devices connect to them in a star fashion.
A hybrid topology can have two or more layers of the network, such as layer three and layer four. In a hybrid network, the different layers of the network do not share the same underlying technology stack.
Traditionally, the cloud and edge tiers were different technologies. A hybrid network would combine these two distinct components into one fabric, enabling it to provide high speed and low latency while also improving network reliability.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
In recent years, hybrid topology has become popular for computer networks because of its many advantages.
One advantage of hybrid topology is that it can be easily adapted to changes in business needs.
For example, if a company decides to add more branches, the hybrid topology can be easily modified to accommodate the new branches. In contrast, star topology can be difficult to modify when required changes.
Another advantage of hybrid topology is that it provides redundancy. If one device in the network fails, the other devices can still communicate with each other and share resources.
In contrast, mesh topology does not provide redundancy; if one device fails, the entire network will fail.
Finally, hybrid topology is scalable, making it easy to add hardware or network components as needed.
As such, it is sought after by many people and companies in the networking field. It combines the advantages of different topologies, making them equally effective.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
The main disadvantage of hybrid topologies is that they are more complex and challenging to manage than the individual topologies that make up the hybrid. Because hybrid networks have multiple layers, their processing becomes more complicated.
In addition, they can be less reliable and less scalable than the individual topologies.
Hybrid topologies require expensive hubs that are intelligent enough to work with different architectures.
Hybrid networks also tend to be expensive, and the whole system won’t work if one part is down. They are, however, a good choice for larger networks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, network topologies are important to understand when designing and creating a network.
There are three main types of topologies: bus, star, and mesh. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when choosing the right topology for a network.
Network administrators should be familiar with the different topologies and how they work to create a network that meets their organization’s specific needs.