FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
When you create a video file, then you want that it should be watched by most people and should be supported by maximum devices and media player.
So, choosing the right video file format is extremely important, which further depends on the combination of codec and container.
Video file formats are a bit different from other file formats.
The other file format such as document and spreadsheet doesn’t have many dependencies. You don’t need to think twice before saving it on your devices.
But, before saving video files, you have to consider multiple factors.
Additionally, you need to ensure whether your video file format will work where you want to be.
Moreover, a video file will have at least one video, and one audio track referred to as “stream.” So, a video file can have multiple video and audio streams.
We need to understand how these multiple videos and audio streams are processed and put together in a video file.
Let’s look into what video file format is and the difference between container and codec in file format.
What is the video file format?
A video file format is essential when you want the video file to be transmitted over a network, upload to a different platform like YouTube, and be played by various media players.
Further, the size and quality will determine the video file format.
Moreover, the quality and file size will depend on two factors.
The file size you choose
The video file size will grow when you increase the video resolutions.
So, it is important to have the correct file size, which can be stored, transit and played easily in a media player.
When you talk about file size, we generally need a codec, compressing or decompressing your video stream.
It is important to decide the correct codec for your video stream to be supported by your media player and easily transmitted.
How do you put together all files in one package?
A video has multiple parts which are put together to form a final package.
It will have a video stream, audio stream, and some other additional information like subtitles, metadata, and so on.
So, we need a container that can put together and bundle multiple parts.
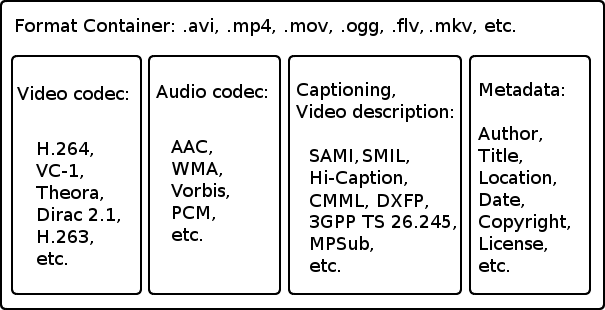
When you combined the two factors, a video file format will have two things: codec and container.
What is the Codec?
A Codec is an algorithm used to compress and decompress video or audio streams to be stored and playback on a device.
In other words, it is a method used to encode and decode data and the protocol used to compress data, especially video.
The compressed video stream makes the file size smaller, making it necessary and efficient for the right situation.
There are several types of codecs; each has its own strengths, weaknesses, and peculiarities.
Moreover, the ratio of video/audio quality to file size depends on the codec’s efficiency.
The video cameras or screen recorder automatically determine the codec, which may or may not be controlled by settings.
The most popular codecs for digital videos are h.264, and for DVD media and TV, it is MPEG2.
When you use video editors for editing videos, then they automatically take care of codec stuff.
Let’s look into some of the most common video codecs.
Popular video codecs
HEVC/H.265
H.265, also referred to as HEVC, is the most efficient and preferred codec for 4k video streaming. Most major streaming video players support it.
It offers high-quality compression with relatively small file sizes. The downside of H.265 is that it is facing some compatibility issues with some of the players.
H.264
H.264 is a widely accepted codec developed by BluRay discs, and all kinds of players and streamers use it.
It offers efficient compression with good image quality but less efficient compared to H.265.
H.264 is the safest option if you don’t care much about file size.
MPEG 4
MPEG 4 is another popular and most common codec for online streaming and video players.
But, it is less preferable over H.264 or H.265. You will find that there are multiple standards within MPEG 4.
DivX and Xvid
DivX and Xvid are some of the oldest codecs which are efficient in compressing the video stream by retaining the maximum video quality.
But, you won’t get a much smaller file size like H.264 or H.265.
What are Containers
Video containers combined all video or audio stream along with additional information like subtitles, metadata. It is also referred to as “format.”
Simply, the container act as a “Wrapper” that can contain actual media stream files. It takes care of the packaging, transport, and presentation of the video stream.
Each video container supports certain video codecs only. For instance, the AVI container is minimal, with only one video stream and one audio stream.
The MKV container is very flexible and supports multiple streams but not compatible with all devices. The .MP4 standard is a widely accepted container that supports multiple streams and devices.
The VLC video player is the most commonly used video player, which accepts almost all file formats and codecs.
When you use video editing software, then it will automatically choose compatible pairings.
When you have edited your video and want to export it, you can use the most preferred file type (container) MP4.
Additionally, it would help if you decided on the codecs and containers before making or editing the videos not to have issues when you render your final videos.
Let’s look into some of the common containers.
Popular video containers
MP4
The .MP4 container is supported by almost all media players and is also used in the largest streaming services like YouTube and Vimeo.
It can use codecs like H.264, H.265, all versions of MPEG-4. The video using .MP4 container can have a smaller size and retain high quality.
AVI
AVI is one of the oldest and widely accepted video file formats. Moreover, it can accept almost every range of codecs.
Additionally, the AVI file format can be played in all types of video players.
The downside of the AVI container is that it will result in a larger file size which won’t be suitable for streaming or downloading.
MOV (Quicktime)
The MOV container is developed by Apple and uses Quicktime player. Moreover, the MOV file format will output high-quality video but with a fairly large file size.
The downside of the MOV file format is that you cannot access it from non-Quicktime players.
FLV (Flash)
The FLV container is made for Adobe Flash player. It can have files of tiny size and widely accepted as a browser plugin.
Nowadays, flash videos and players are not popular, and there is a significant decline in users.
WMV (Windows Media)
The WMV container can have a file of the smallest size, which can be sent through email or used where there are limitations in file size.
However, because of the smallest size, you will have low video quality.
Which Video file format should you choose?
The best file format will depend on your specific needs. You need to understand what your audience is looking for and which file format will maximize benefits.
When you are concerned about distribution and delivering video files, then a combination of .MP4 and H.265 will be best.
If you are more concerned about compatibility issues, you can replace H.265 with H.264.