FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
We know that WiFi is the most readily available option to connect to the Internet, but most businesses and home networks still rely on Ethernet.
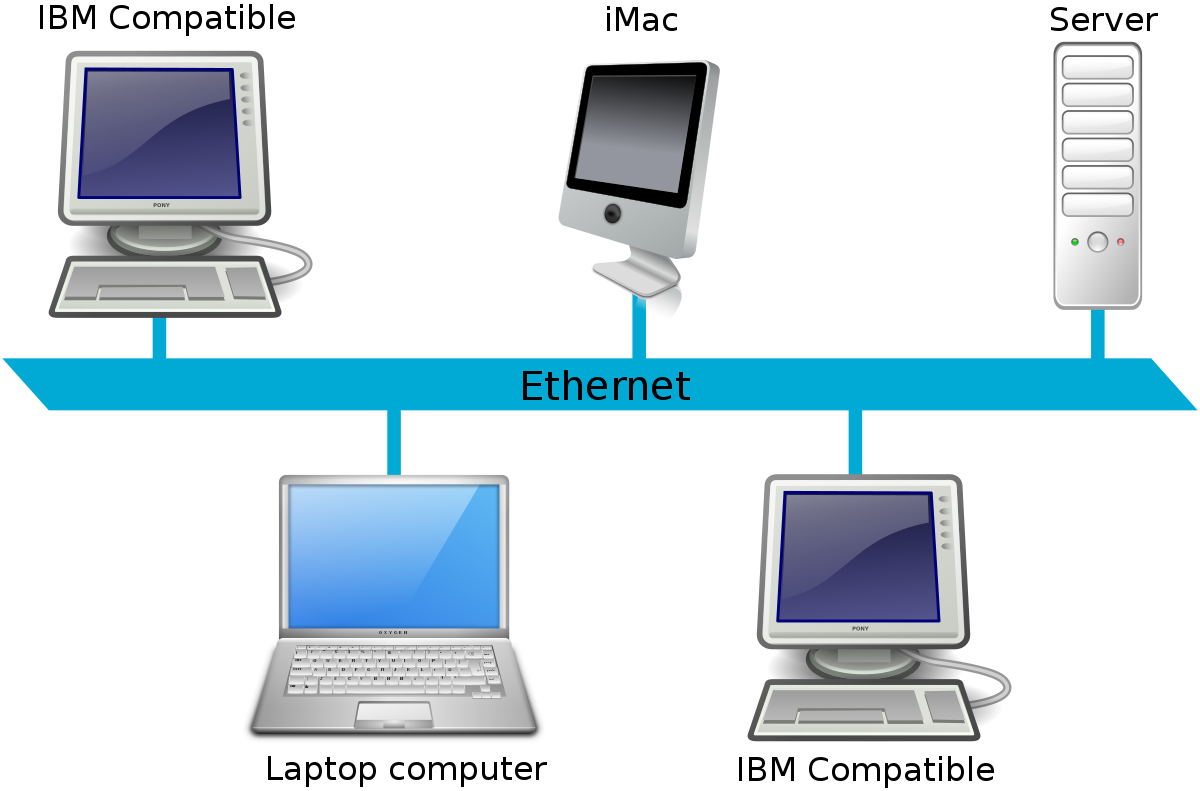
Ethernet is the most commonly used technology in Local Area Network (LAN) that connect computer and devices in a small area.
We will look into in-depth Ethernet technology and Ethernet network. Also, the type of Ethernet networks and cables we need to use to build LAN.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is a standard communication protocol technology for connecting devices in a wired local area network (LAN) to enable communication.
In other words, Ethernet is a system that uses the protocol to transmit and receive data in a wired local area network (LAN).
The function of Ethernet is to provide uninterrupted high speed, network security, and control which is helpful in businesses, video streaming, and virtual communication.
It makes it difficult for unknown devices to hijack bandwidth and access network data.
Further, Ethernet helps develop a local area network (LAN) that can spread up to 10 kilometers.
It uses cables such as Cat5, Cat6 to transfer data from LAN to the Internet.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) implemented Ethernet and defined IEEE standard 802.3 as Ethernet standard.
Ethernet protocol 802.3 describes network policies and states the elements of how each device can communicate in a LAN (Local Area Network).
Moreover, you would have used Ethernet technology in your offices, bank, and home without knowing its actual purpose.
Also, most laptop and desktop computers come with an integrated Ethernet card that is ready for LAN connectivity.
What is an Ethernet network?
Ethernet network creates a local area network (LAN) by combining multiple computers or devices connected governed by Ethernet policies and protocol.
The computer or devices are connected through fiber-optic cables in a Wired Ethernet network. Also, an Ethernet network uses topologies like a star, bus, ring, and more.
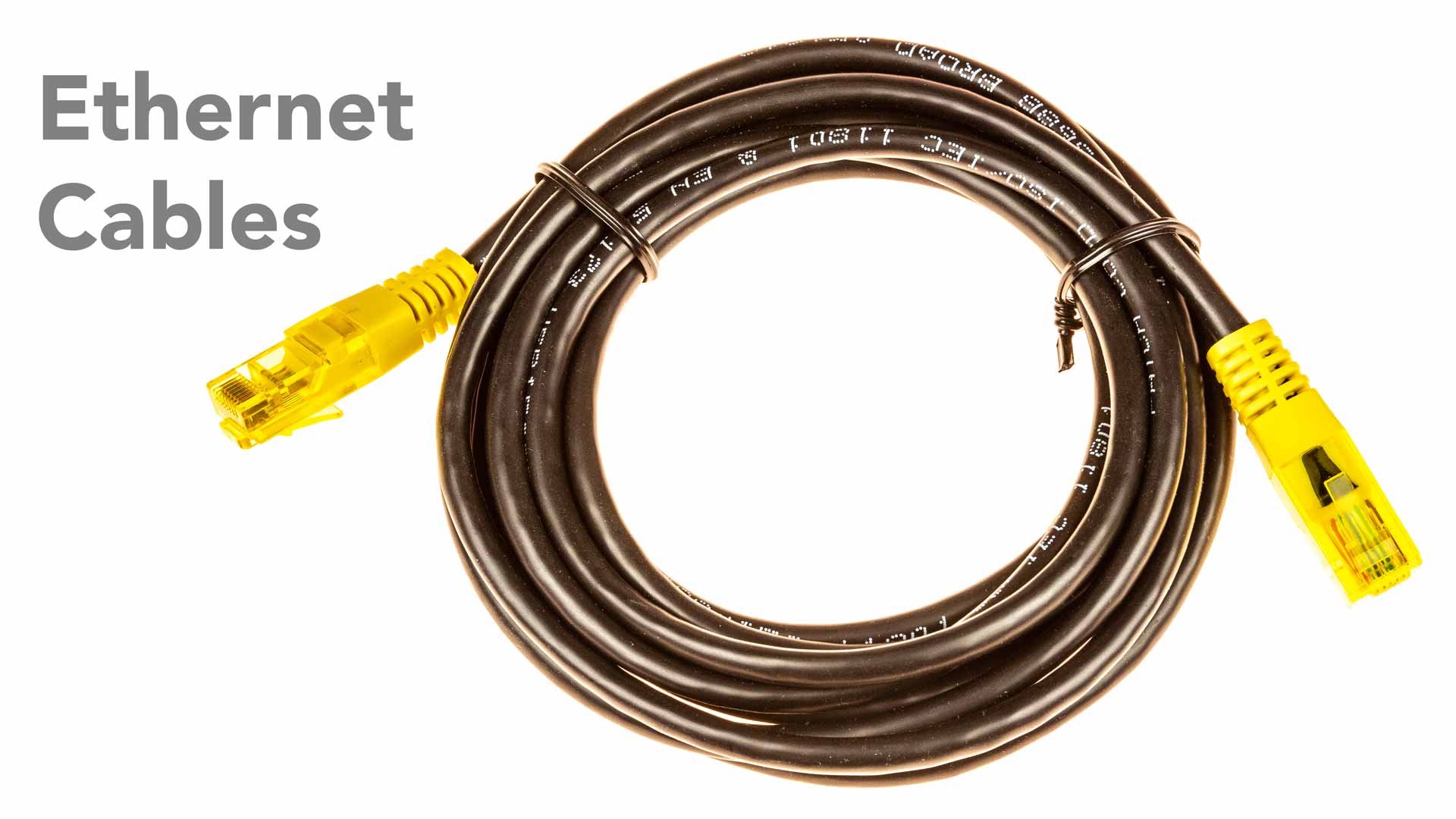
What is an Ethernet cable?
An Ethernet cable is a network cable used for wired Ethernet networks to connect computers to a router or modem.
One side of the Ethernet cable is connected to the Ethernet port of the device and the other end to the router or modem.
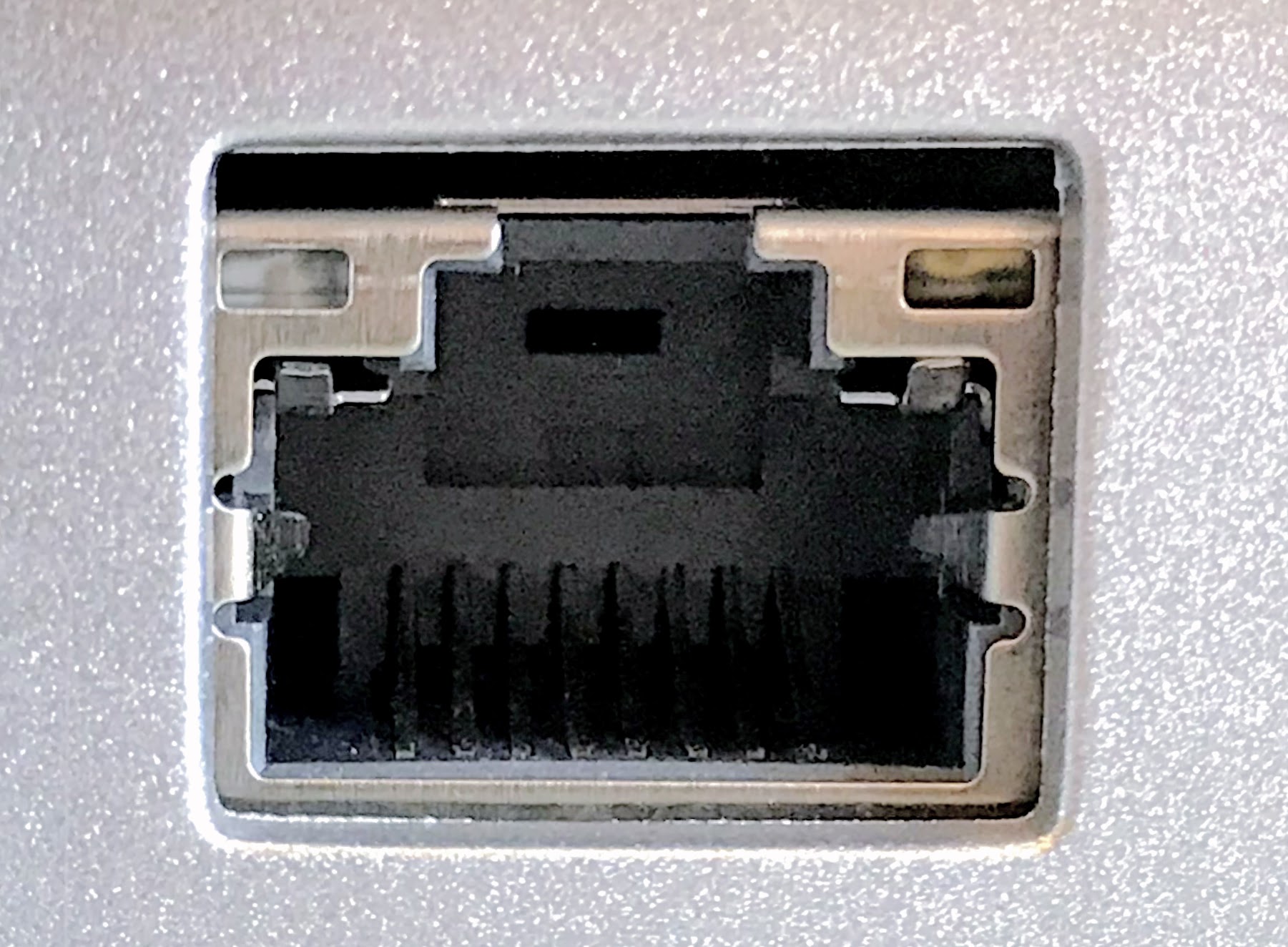
What is an Ethernet port?
An Ethernet port, also refers as a socket or a jack, is the equipment used to connect a networking device to an Ethernet network using an Ethernet cable.
The networking device can be your computers, laptops, router, switch, or hub.
The Ethernet cable has an Rj45 connector to the Ethernet port.
Ethernet port is further connected to the network adapter of the computer. Also, the network adapter is either embedded or attached to the motherboard.
The network adapter is also called an Ethernet Card or Network Interface Card (NIC).
How does Ethernet work?
Ethernet working is based on IEEE 802.3 standard and how the OSI model facilitates the operation of the physical layer (Layer 1) and data link layer (Layer 2).
The OSI model consists of seven layers, and each layer comprises various communication protocols. All layers work together to transfer information from one computer to another.
Moreover, data transmission takes place in the form of packets and frames.
The packets contain the information of the client (sender) and receiver (server). The information includes IP address, browser agent, and device version.
The packet is first transmitted from the application layer (Layer 7). The user accesses the data through the browser or mail client until it reaches the lower layer (Datalink and physical layers).
The lower or the physical layer is closest to your device, including Network Interface Card (NIC) or Network Adapter to connect to Ethernet cable.
The transmission of data in the lower layer takes place in the form of the frame. The frame includes information like MAC address, QoS, and error correction.
When the frame is transmitted to the upper layer, it is wrapped in a packet.
When the data is transmitted from one device to another, there will be hubs or switches in-between.
The hub or switches copies data from the sender and transmit it to the intended devices. It intelligently manages traffic from sender and receiver and improves efficiency and security.
Additionally, IEEE has developed Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) protocol to avoid packets collision and connectivity problems.
Types of Ethernet networks
Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that can transmit data up to 100 Mbps using twisted-pair cable or fiber-optic cable.
Moreover, Fast Ethernet uses 10BaseT cabling and is based on CSMA/CD Media Access Control (MAC) protocol. Additionally, the data can transmit in the range of 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that can transmit data at the rate of up to 1000 Mbps using twisted-pair cable or fiber-optic cable.
It uses Cat 5e twisted-pair cable to achieve high data transfer speed.
10-gigabit Ethernet
10-gigabit Ethernet is an Ethernet network that can offer 10 Gbps data speed through Cat6a, Cat7 twisted-pair cable, or fiber-optic cables.
Moreover, it is not widely used compared to Gigabit Ethernet and Fast Ethernet.
Switch Ethernet
Switch Ethernet is a type of Ethernet network that requires equipment such as a network switch or hub to forwarding data from one device to another.
It uses network cable instead of crossover cable and can perform data transmission tasks efficiently.
Moreover, switching Ethernet doesn’t affect the performance of other devices on the same network.
Additionally, it supports data transfer rates in the range of 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps for fast Ethernet and 1000 Mbps to 10 Gbps for Gigabit Ethernet.
The function of Switch Ethernet is to use a switching mechanism and filtering techniques to transfer data to the intended device.
Further, it uses star topology to organize a network around a switch.
Different types of network cable
The different types of network cable are required to perform various tasks, and the design differs in terms of the diameter of the cable.
- 10Base2 is a type of cable that uses thin coaxial cable
- 10Base 5 is a type of cable that uses thick coaxial cable
- 10Base-T uses a Twisted-pair cable and can achieve a data speed of up to 10 Mbps
- 100Base-FX is a type of cable that uses multimode fiber optic to accomplish a data speed of up to 100 Mbps.
- 100Base-TX is a type of cable that uses a twisted-pair cable, but it can achieve ten times greater speed up to 100 Mbps.
- 1000Base-T uses Cat 5 double twisted-pair cable to speed up to one Gigabit per second.
- 1000Base-SX is a type of multimode fiber optic that uses a short wavelength signal of 850 nanometers.
- 1000Base-LX is a type of multimode fiber optic that uses a long-wavelength signal of 1350 nm.
Advantage of Ethernet
Ethernet is inexpensive
Ethernet is a popular network technology that grows with time and is still an inexpensive option compared to other competing technology.
High level of performance and stability
Ethernet has evolved from the past and provides high performance, stability, and sustainability.
Ethernet speed
Traditional Ethernet supports a speed of up to 10 Mbps. But, as the technology evolved, Ethernet data transfer speed increased up to 100 Mbps.
Moreover, the current version of Ethernet technology can support data transfer speed up to 400 gigabits per second (Gbps).
Security
Ethernet network is secure because you can control who can access LAN. Also, if anyone is not connected to the network, they have no access to services or data.
Disadvantages of Ethernet
Poor accessibility
It is difficult to add a new user to the Ethernet because it requires empty router ports and extra cables.
On the other hand, it cannot connect to most mobile devices like smartphones and tablets because of Ethernet ports’ unavailability.
Transportability
Ethernet network is challenging to transport from one location to another because it requires new installation and wiring of Ethernet cable.
Expansion cost and time
Ethernet networks can be built up using equipment that can be expensive for initial installation and future expansion.
Further, the professional is required to install and expand the network and can take a considerable amount of effort and time.
Difference between Ethernet and the Internet
Ethernet and Internet both allow devices to communicate with each other, but some difference makes them distinct.
Connection range
Ethernet is built up in small spaces such as office buildings, apartments, and society and can go up to 10 kilometers. It comes under Local Area Network (LAN).
But, Internet has a more comprehensive network, and there is no limit to its expansion. Internet-connected devices in Wide Area Network (WAN) cover the entire world.
Network size and administration
Ethernet network size is small, and few administrators are needed to manage the whole network.
But, the Internet is vast, and one can administer only a tiny part of the network.
Security issue
Ethernet is more secure and safe than the Internet. If you don’t have access to an Ethernet network, you cannot access data and services.
But, the Internet is not that secure and poses a severe threat to data transmission and access from outside.
Difference between Ethernet and Wi-Fi
Signal stability
Wired Ethernet network provides signal stability because of no interference, disconnections, and slowdowns. It is reliable when you transfer massive data from one computer to another.
Wi-Fi signals have an interference issue because of connectivity through radio frequencies. You can face interference issues because of big walls, tunnels, and electronic devices.
Flexible and secure
Wired Ethernet is flexible and secure when transferring data up to 100 meters distance. It is fast and flexible for your businesses, game console, or desktop gaming.
You can also control and maintain security in your local network and prevent any unwanted security breaches.
Wi-Fi is accessible to a more extensive network, but it is more vulnerable to potential threats.
Cost
Wired Ethernet is more costly compared to Wi-Fi. If you want to set up a safe, private, and stable LAN network, you require servers, firewalls, modems, switches, hubs, and professional installation and maintenance.
Further, the cost and maintenance will increase with installing a new workstation.
Mobility issue
With wired Ethernet, you will face mobility issues because you cannot use mobile devices like smartphones, netbooks, tablets, e-readers, and portable gaming systems.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi has no mobility issues and can connect to many mobile devices. You can even increase data speed with an 802.11ac standards router that supports dual and tri-band Wi-Fi routers.
Which one to choose? Wired Ethernet or Wi-Fi
The choice depends on your requirement, preferences, and budget.
If your requirement and preferences are browsing, HD streaming, and game, which doesn’t require many resources, then a Wi-Fi router with dual-band is sufficient.
But, if you are looking for online business, an online game where stability and reliability matter the most, then wired Ethernet is preferable.