FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
In Networking, transmission media are necessary to form a network. They are considered as a physical path between sender and receiver.
When you communicate from one node to another node, the transmission medium acts as a physical connection or an interface between the sender and receiver.
What is Transmission Media?
Transmission Media is the communication channel in the physical path that transfers information from the sender to the receiver.
The transmission can be coaxial cables, optical fibers, or electromagnetic waves.
What is the role of transmission media in a network?
The role of transmission media is to carry information through physical means from transmitter to receiver in bits.
The bits in the copper-based network are in the form of electrical signals, whereas the bits in the fiber-based network are in the form of light pulses.
The wireless medium carries bits in electromagnetic waves by varying the amplitude or frequencies of the wave.
Moreover, the transmission differs by their properties, such as bandwidth, delay, cost, and ease of installation and maintenance.
You will find transmission media in the lower layer of the OSI model that is the Physical Layer.
The transmission media is mainly divided into two types:
- Guided Media or Wired Media or Bounded Transmission Mode
- Unguided Media or Wireless Media or Unbounded Transmission Mode
Factor affecting transmission media
There are mainly three factors that affect the designing of transmission media.
Bandwidth
The transmission media can have a higher data transmission rate when it provides greater bandwidth keeping the other factor constant.
Transmission Impairment
Transmission Impairment defined the quality of the signal and how much the transmitted signal is not identical to the received signal.
The transmission impairment is further divided into three parts.
Attenuation
Attenuation is the process in which the strength of the signal decreases with distance because of the loss of energy.
Distortion
Distortion is the process in which the signal’s shape further affects the frequency of the signal and its propagation speed.
Due to distortion of the signal, the transmitted signal will delay reaching the receiver end.
Noise
Noise is defined when adding an unwanted signal with the transmitted signal over a transmission medium.
Interference
An Interference is when the transmitted signal is disrupted in the communication medium because of an unwanted signal.
Understanding Guided Media and Unguided Media
The transmission media is classified into two types: Guided media or Wired media and Unguided media or Wireless media.
The medium characteristics are more significant in Guided media or Wired media. But, the signal characteristics are more important in Unguided media or Wireless media.
Guided media or Wired media
The Guided media is also referred to as Wired Media or Bounded media.
The signals transmitted in guided media are transmitted through physical links in the restricted thin path.
Additionally, the bounded media are the cables that have physical existence and are limited to geographical location.
The guided media or wired media main features are:
- High-speed transmission
- Secure transmission
- Suitable for small distances.
There are mainly three types of guided media or wired media.
- Twisted Pair Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Optical Fibre Cable
Each of the above-wired media differs in characteristics like transmission media, physical appearance, the effect of noise, cost, and more.
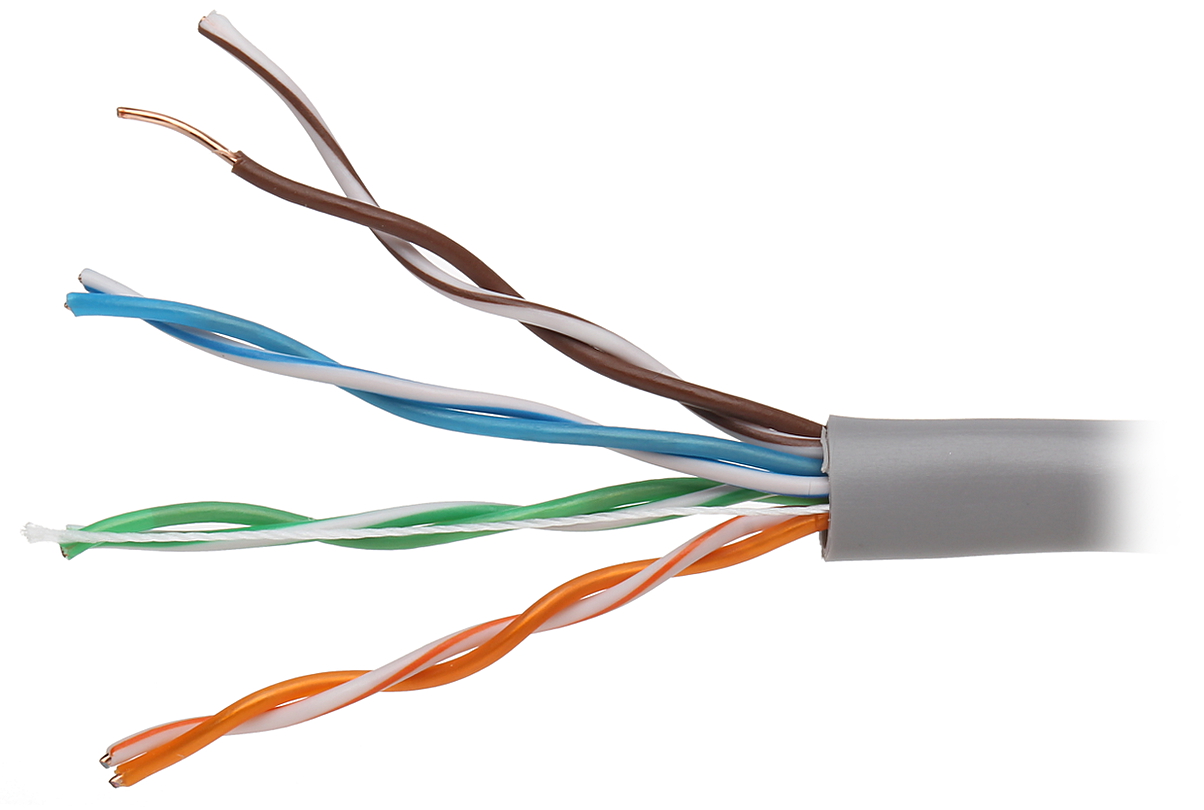
Twisted Pair Cable
A twisted pair cable consists of two separate insulated copper wires twisted together to cancel out electromagnetic interference from external sources.
Further, the insulated copper wires are bundled together in a protective sheath.
The twisted pattern helps to reduce the noise interference and error rate during data transmission. It further improves the performance by containing the electromagnetic field within the pair.
Also, the number of turns per foot in twisted pair cable determines the degree of noise reduction.
Advantages and disadvantages of Twisted Pair Cable
The advantages of twisted pair cable are to reduce the radiation of electromagnetic energy and improve the strength of the signal over a distance.
The disadvantage of a twisted pair cable is that the maximum transmission speed is limited.
Also, it tends to lose more power over distance when using a high-bandwidth application.
The high bandwidth in twisted pair cable will have high frequency, further increasing the electromagnetic field radiation impacting the adjacent pairs to a greater extent.
The twisted-pair cable is divided into two parts:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cable is a cable designed to minimize electromagnetic interference and crosstalk without a physical shield.
Moreover, twisted pair design helps to balance signal transmission. Further, varying the amount of twists in twisted pairs can help in reducing crosstalk.
It was designed by twisting two individual wires around each other to form single pair. Further, the twisted pairs are again twisted around each other.
It is up to four twisted pairs of copper wires found inside the UTP cable. In addition, each twisted pair is color-coded to make the identification easier.
The advantage of using a UTP cable is that it is cheap and easy to install. Also, the disadvantage of using a UTP cable is that you cannot use it for long-distance because of attenuation.
You will find that UTP is further divided into five categories.
- CAT3: Deployed for phone lines and support 10 Mbps for up to 100 meters
- CAT4: It is used in a ring network and supports 16 Mbps for up to 100 meters.
- CAT5: It is used in Ethernet-based LANs (2 twisted pairs) and supports 100 Mbps for 100 meters.
- CAT5e: It is used in Ethernet-based LANs (4 twisted pairs) and supports 1 Gbps for 100 meters.
- CAT6: It is used in Ethernet-based LANs and data center networks consist of 4 tightly wound twisted pairs. It supports 1 Gbps for up to 100 meters and 10 Gbps for up to 50 meters.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
The Shielded Twisted Pair is a type of cable designed to enclose twisted pair in a protective metallic shield to provide greater protection from electromagnetic and radio frequency interference.
The advantage of using STP cable is that it provides a higher transmission rate with low interference of electromagnetic waves.
The disadvantage of using STP cable is that it is more expensive, difficult to install, and has a higher attenuation rate.
Coaxial Cable
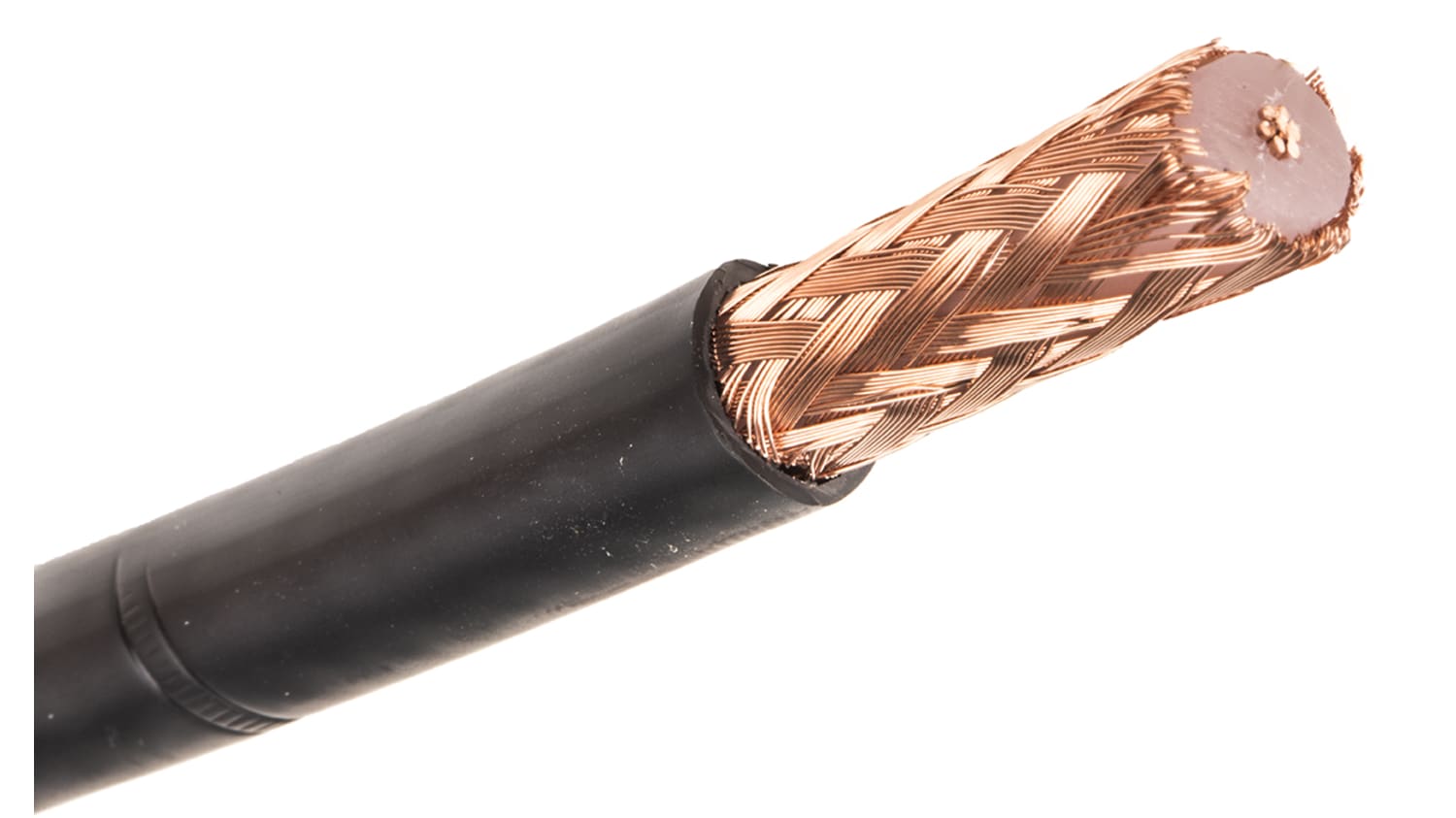
A coaxial cable is a type of cable that consists of two conductors running parallel to each other.
The inner conductor is usually made of copper, and the outer conductor is made of braided copper mesh separated by the non-conductive cover.
Further, the inner copper conductor is responsible for transferring data, whereas the outer conductor is the braided copper mesh that protects the signal from electromagnetic interference.
The non-conductive material in-between inner and outer conductors are called a dielectric insulator.
Coaxial cable is most commonly used by cable operators, telephone companies, and Internet providers. It is preferred in services like data, video, and voice communications to customers.
The shielded design of Coaxial cable is beneficial in transmitting data quickly without being much exposed to electromagnetic interference and other environmental factors.
You will find most common cable sizes are RG-6, RG-11, and RG-59. Here, RG is Radio Guide, the measurement unit.
Moreover, the Coaxial cable transmission mode is of two types
- Baseband mode (Dedicated cable bandwidth): It will transmit a single signal at high speed.
- Broadband mode (Cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges): It will transmit multiple signals at once.
Advantages and disadvantages of Coaxial cable
Advantages of Coaxial cable
- It supports high-speed data and bandwidth.
- Cable shielding is better than Twisted pair cable
Disadvantages of using Coaxial cable
- It is expensive compare to Twisted pair cable and can disrupt the entire network if any fault occurs.
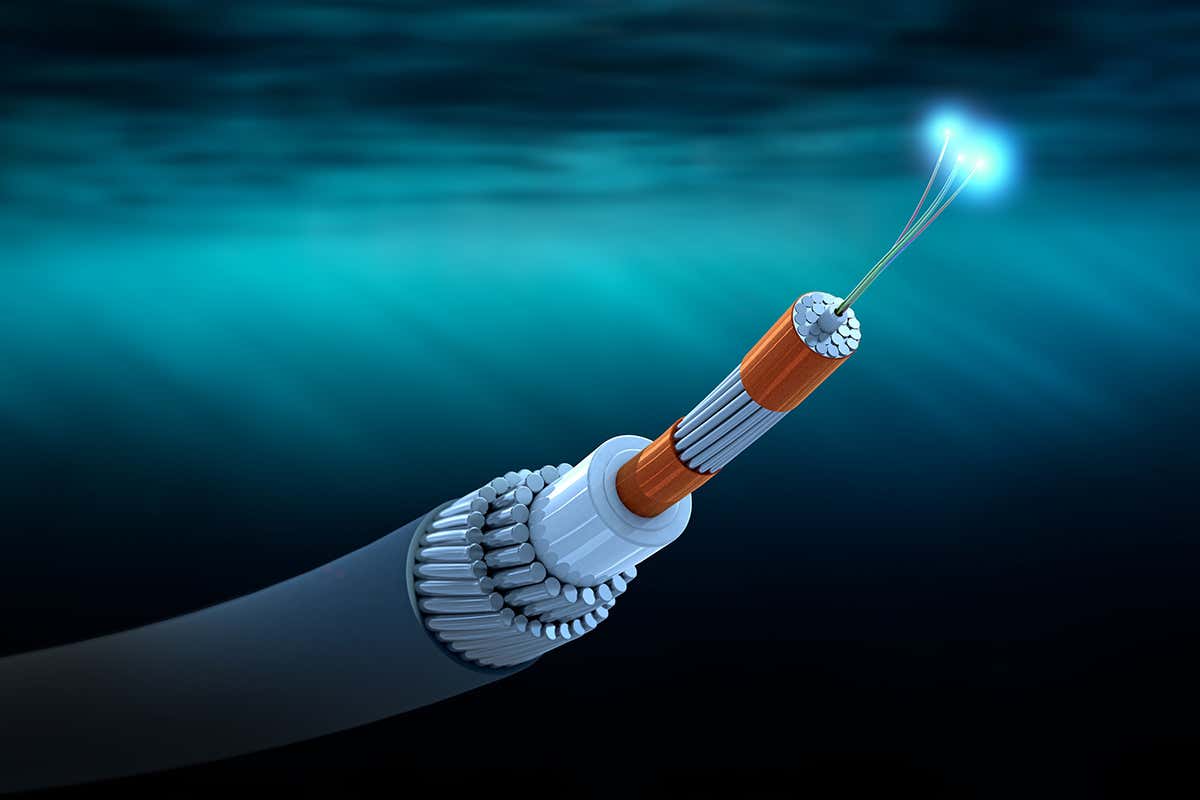
Fibre Optic Cable
Fiber Optic Cable is a type of cable that uses the light signal to transmit data through strands of glass.
These strands of glass are bundled together to called optical fiber. Moreover, each strand is having a diameter of human hair.
Also, each strand of glass (optical fiber) can carry data in both directions but of different wavelengths.
Additionally, the Fiber Optic cable is free from Electromagnetic Interference and wiretapping. It is mainly considered for broad-band communication.
Also, the Fiber Optic cable can carry a bandwidth of more than 2 Gbps (Gigabytes per second).
The structural elements of Fibre Optic cable are consist of three parts.
The core of Optical Fiber
The center of optical fiber consists of strands of glass called Core. The Core is a part that transmits light.
Also, the bigger the area of the Core more transmission of light possible.
Cladding of Optical Fiber
The Cladding surrounds the Core is made from less pure glass. Moreover, the material of Cladding is having a lower index of refraction than the core.
The functionality of the lower refractive index of Cladding can cause light to be confined to the fiber’s core.
In this way, light waves are transmitted through the fiber for a long distance with the lowest attenuation.
Jacket in Optical Fiber
The Jacket in Optical Fiber is a protective coating consist of plastic.
It will preserve the fiber strength by giving extra protection and also help in absorbing shock.
Advantages and disadvantages of Fiber Optic Cable
Advantages of using Fiber Optic Cable
- The fiber optic cable has better bandwidth and can carry more data as compared to copper cable.
- Fiber Optic Cable can have a higher speed because it carries your data in the form of light.
- The data reliability in a long distance can be possible with fiber optics because it can withstand any temperature change and handle pull pressure.
- Fiber Optic Cable is immune to electromagnetic interference, less signal attenuation, and resistant to corrosive materials.
Disadvantages of using Fiber Optic Cable
- Fiber Optic Cable is difficult to install and maintain.
- It will cost you more because it needs additional optical components for installation.
Unguided Media or Wireless Media
Wireless Media or Unguided Media is a type of transmission media in which the signal is broadcasted without the need for guided media through the air.
In other words, Unguided transmission media is a type of media that can transmit electromagnetic waves without any assistance from a physical medium.
There are mainly three most used Unguided Media or Wireless media
- Radio Wave
- Microwave
- Infrared Wave
The advantages of using Unguided media are:
- You can expand your network without any problem and disturbance.
- You can access your network remotely.
The disadvantages of using Unguided media are
- It is less secure, and one can face major security issues
- Speed is variable, not consistent, and can have less speed compare to Guided media.
The unguided media is broadly classified into three heads:
- Radio Waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared wave
Radio Waves
The radio wave is a type of electromagnetic wave which carries information through the air and having a lower frequency and highest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Moreover, radio waves can be transmitted and propagated in all directions.
The frequencies of the Radio wave range from 30 Hz to 300 GHz, whereas the wavelength can be 1mm (smaller than the grain of rice) at 300 GHz and 10,000 Km (more than the radius of the earth) at 30 Hz.
The Radio wave can be useful in multicasting where there would be one sender and multiple receivers. Also, the Radio wave is most popular in the mobile cellular phone, FM radio, Television.
The advantage of using radio waves is that they can easily travel through larger distances and penetrate larger obstacles.
Also, the sending and receiving antennas need not be aligned.
To understand better, we can divide Radio waves into two-part. The one part consists of Radio waves having lower frequencies and higher wavelengths, and the other part of consists of higher frequencies and lower wavelengths.
Radio waves (lower frequencies and higher wavelength)
The lower frequencies radio waves such as VLF (Very Low Frequency), LF (Low Frequency), MF (Medium Frequency) can travel up to 1000 KM over the earth’s surface.
Moreover, because of the larger wavelength, it can penetrate easily through large obstacles.
Also, the radio wave at lower frequencies can travel larger distances, but it decreases its power with distance.
Radio waves (higher frequencies and lower wavelength)
The radio wave having larger frequencies can travel in a straight line, bounce back, and maintain more power.
In contrast, the higher frequencies radio waves such as VHF (Very High Frequency) and HF (High Frequency) can travel straight in the direction of the earth’s atmosphere.
In addition, when the high frequencies of radio waves reach the Ionosphere of the earth’s atmosphere, it is reflected.
The disadvantages of high frequencies radio waves are that it is more prone to the absorption by rain and other obstacles.
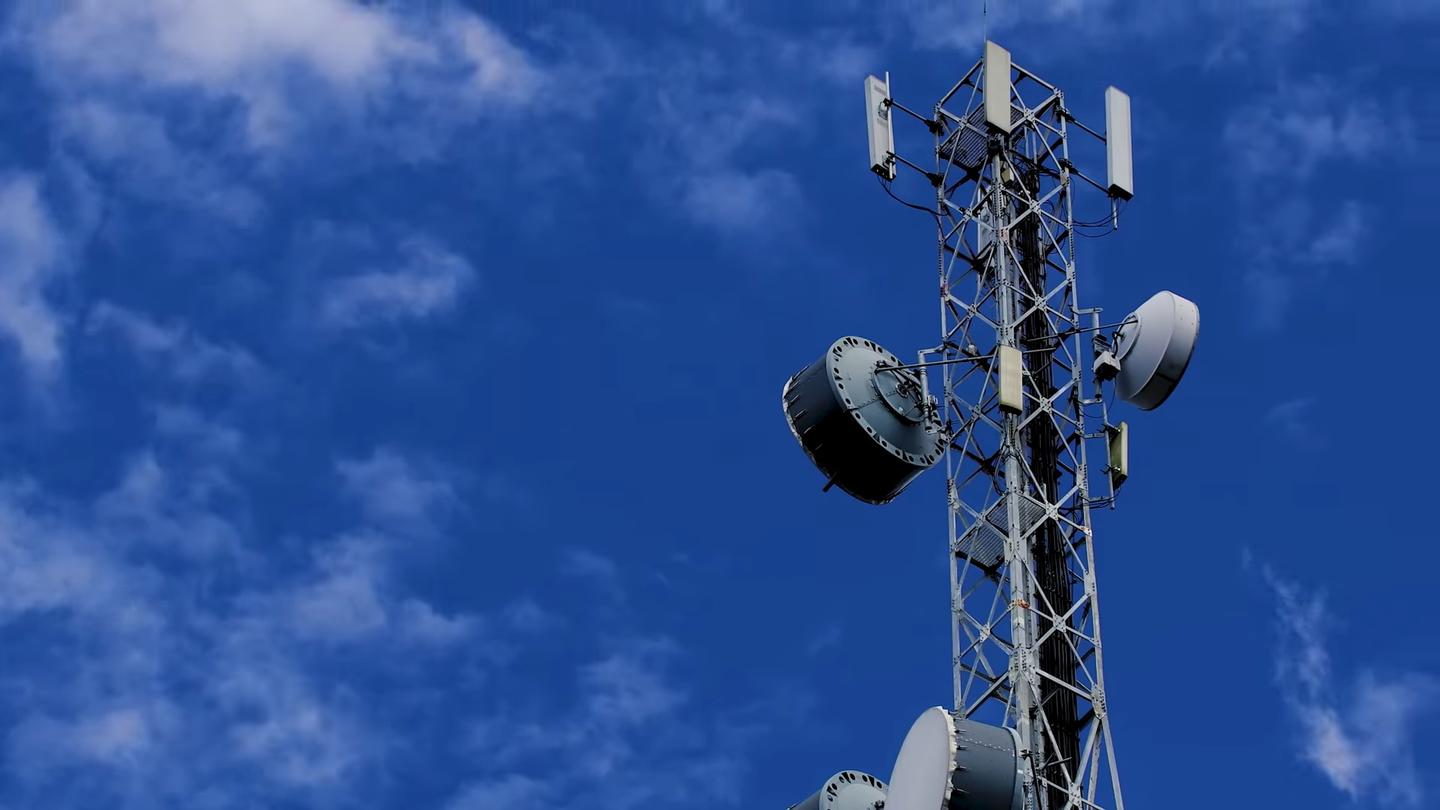
Microwave Transmission
Microwave transmission is a type of unguided transmission that carries information with wavelengths ranges from 1m to 1mm in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Moreover, microwave transmission is a line-of-sight wireless communication technology that uses high frequency and high-speed wireless connections to send and receive voice, video, and data information.
The advantage of using microwave transmission is that it can carry a large amount of data at a relatively low cost.
The disadvantages of using microwave transmission are that it gets affected by solid objects because of the high-frequency wave. Also, it gets affected by other electromagnetic interference.
Microwave transmission is different from radio wave transmission. A microwave uses shorter distances while radio waves travel long distances.
Additionally, a radio wave is propagated through sky mode while the microwave uses the line-of-sight propagation.
Infrared wave
An infrared wave is an electromagnetic wave whose wavelength is longer than visible light and shorter than microwave and radio waves.
Its frequency lies between 300 GHz and 400 THz in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Moreover, the infrared wave is used in a very short-range communication purpose such as remote control, monitoring application, security systems, and thermal imaging cameras.
Also, the transmission of data from one point to another point is referred to as beaming.
The advantage of using infrared transmission is that it requires minimum power to operate, and the setup cost is low.
The disadvantage of using infrared transmission is that it has a small range, and data transmission speed is slow. Also, it requires line-of-sight.