FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
It would be unclear for many to understand the differences between a hub, Switch, and Router.
However, the term is often misused when all three devices are integrated into a single device.
The Hub, switch, and Router plays a crucial role at various levels in the networking world, but the three devices’ functionality differs.
All three, Hubs, switches, and routers, will let you connect multiple devices in a network and outside the network.
Each device consists of multiple ports that let you plug the cable to establish a connection.
Here, we will look into how Hub, Switch, and Router are different and when to use which device.
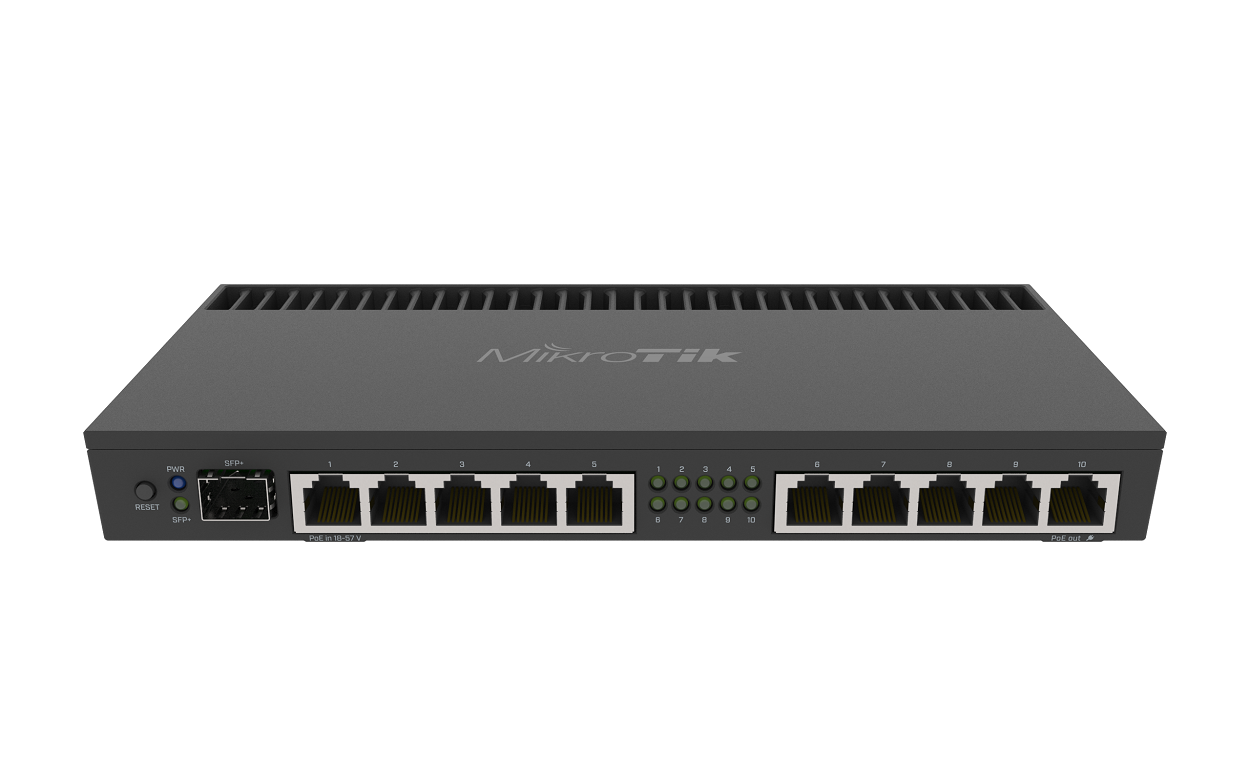
Understanding Hub, Switch, and Router
Network Hub
A network hub is the most commonly used device to connect multiple computers or devices in a network.
Moreover, a hub is the least intelligent compared to switches and routers.
Its work is straightforward. When the Hub receives data from one device or computer, it will forward the same message to all the connected devices or computers.
Also, it doesn’t matter; the message belongs to which computer.
It will forward messages or data to all the connected devices, and it is up to machines or computers to accept them or reject them.
Similarly, when any computer is connected with a network hub response to the message, it will go to all the connected devices.
If your devices are connected with the Hub, there would be no data privacy, and your activity will be transparent with other connected devices.
As a result, one computer can see the activity of all other computers connected with the Hub.
So, any traffic or data received in one Hub port will also be received by other hub ports.
It is used because it is quick, easy to connect, and less costly than switches and routers.
Ethernet Switch
The Switch is far more intelligent than Hub. Like Hub, it is also the central connection point for all the connected devices in a network.
Moreover, Switch knows each connected device’s location, and when the message receives, it will be sent to the destination address.
After reading the destination address, it will send the messages or data to the destined address.
Initially, Switch didn’t know anything about connected devices.
So, when the Ethernet Switch receives the first message, it will read the sender address to which port it belongs.
Similarly, when it receives messages or data from other connected devices, it will learn the port address of those devices.
After knowing each device’s location, it can now direct the message where it is intended to send, rather than every port.
Switches locate the port of each connected device very quickly.
Afterward, Switches read the destination address, do error checking and forward the message to the correct port.
Moreover, Hub broadcast messages to all the connected devices simultaneously, whereas Switch determines the destination address and sends it to that device only.
This makes Switches more efficient and faster than Hub.
Router
A router is a most intelligent and most innovative device when we compare it with hubs and switches.
A router is considered a small computer designed and programmed to understand, manipulate and route internet traffic.
Moreover, the Router also comes with a user interface, which helps you manage traffic and security.
A router usually connects two or more networks; two LANs, two WANs, or a LAN and ISP network.
When the Router receives traffic, it will calculate the best route to send the traffic. Additionally, communication with connected devices and the internet takes place using a network protocol.
The Router’s basic functionality is similar to switches, like locating network traffic and routing the traffic to the correct destination.
But, the router intelligence comes into play in how it routes the traffic. It uses headers and forwarding tables to determine the best path for the data packets.
Additionally, it uses an ICMP protocol (Internet Control Message Protocol), which helps in the two hosts’ communication and configuration at two ends.
A vital function of the Router
Other than routing, the Router has some additional functionality. It has two other important tasks: DHCP and NAT.
The DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. The functionality of this protocol is to assign a dynamically new IP address to the connected device.
This type of IP address, which DHCP assigns, is an Internet IP address or a Local IP address.
Similarly, when the Router first connects to the internet, the ISP will assign an IP address to your Router, known as a Public IP address or External IP address.
Therefore, the Router is the single interface representing your internet devices.
NAT stands for Network Address Translation, whose functionality is to translate the IP address when it crosses the local network to the internet and vice versa.
When you send data packets from your device like a computer to the Router, it will translate your local IP address to a public IP address and then forward it to the internet.
Similarly, when the traffic reaches your Router from the internet, it will translate the public IP address to the local IP address.
From the above process, you can say that the Router acts as a firewall to all the devices on the internet because they cannot communicate directly to your device.
Most Router comes with a switch and hub functionality to enhance the Router’s functionality.
Moreover, the business router has additional software to set up network firewalls and VPN (Virtual Private Server).
You will find two types of routers in the market: Wired and Wireless.
The wired Router uses an Ethernet cable to connect with devices, whereas the Wireless Router uses a radio signal to communicate with Wi-Fi in-built devices.
Hub vs. Switch vs. Router: Differences in Transmission of traffic
In Hub and Switch, traffic transmission is in the form of a frame.
When the Hub and Switch receive the Frame, it will direct it to the connected devices.
The network Hub receives Frame from a computer and will send it to all the connected devices. Moreover, it doesn’t matter whether the Data Frame belongs to a particular device or not.
Additionally, it will also share bandwidth to every port, which reduces its efficiency.
In contrast, the Switches keep the record of the MAC (Media Access Control) address of each connected device.
By using this information, switches know where to send a frame. It will direct the Frame to the correct port.
Unlike Hub, Switches doesn’t share bandwidth, regardless of the number of devices connected and participating in traffic.
So, the user will have access to maximum bandwidth during communication with other devices.
Unlike Hub and Switch, the router route the “packet,” not the “frame.”
Packets contain destination address along with data. The destination address contains the destination’s IP address and other information that helps to reach the destination.
Hub vs. Switch Differences
Hub is recommended over Switch only because it is cheaper than Switch.
The Switch is superior and intelligent compared to Hub because it minimizes the traffic in a network, sends data to the intended devices, and reduces bandwidth usage.
Hub sends data to all the LAN segments, whereas Switch sends data to the intended segment of the LAN.
A hub is in the physical layer (Layer 1) of the OSI model, whereas a switch belongs to the OSI model’s data link layer (Layer 2).
Switch vs. Router Differences
The Router is more innovative and more intelligent than the Switch because it serves multiple networks.
Moreover, the Router can route data packets from one network to another, whereas a switch is only applicable for the LAN (Local Area Network).
A switch can serve only a wired network, which means it can be connected with devices in a network only with Ethernet wire.
On the other hand, the Router can serve both wired and wireless networks, which means you can connect the device either through wire or Wi-Fi.
Router work in the Network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model whereas, Switch belongs to the Data Link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.
Hub vs. Router
Hub supports the basic functionality of moving data from one device to all the devices connected with it. It acts as a passive device that has no software.
Moreover, the Hub’s data transmission takes place through an electrical signal in the form of bits.
On the other hand, the Router knows where the data is coming from and where it should go.
It has the intelligence to map the fastest route and detect any error with the packets.
Besides, the Router is a networking device that transmits data in data packets.
Lastly, the Router comes with multiple functionalities and cost higher than Hub.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a hub, switch, and Router can help you choose your network’s appropriate device.
All three devices have different functionality and can be used for various purposes.
If you are looking for performance and want to connect devices with Wi-Fi, then a Wireless router would be suitable for you.
If you are limited in budget and looking for good performance, Switch can be the better solution.