FTC disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my link.
Did you know that nearly 70% of businesses use proxy servers to secure and manage their web traffic? This is because online security and network management are key. Many businesses get confused about forward and reverse proxy servers.
To make good choices for your web traffic, you must know the difference between these proxy servers. A proxy server is like a middleman between your network and the internet. It makes your online experience safer and faster.
Key Takeaways
- Proxy servers are important for managing and securing web traffic.
- It’s key to know the difference between forward and reverse proxy servers.
- Proxy servers are like middlemen between your network and the internet.
- They help make your online experience safer and faster.
- Choosing the right proxy server is crucial for businesses.
Understanding Proxy Servers
A proxy server is like a middleman between your device and the internet. It handles requests and responses. Your device sends a request to the proxy server. Then, it sends the request to the server you want to reach.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is an intermediary between clients and servers. It gets requests from clients, processes them, and sends them to the right servers. This makes networks more secure and adds features like content filtering and caching.
How Proxy Servers Work
Proxy servers manage data flow between your device and the internet. When you ask for a website, the proxy server gets it for you. This helps hide your IP address, giving you some privacy.
The Role of Proxies in Modern Networks
In today’s networks, proxy servers boost network security. They block bad content, stop unauthorized access, and speed up network access. A top cybersecurity expert says, “Proxy servers are key for secure and fast networks.”
There are many types of proxy servers, each for different needs. Knowing these types helps choose the right one for you.
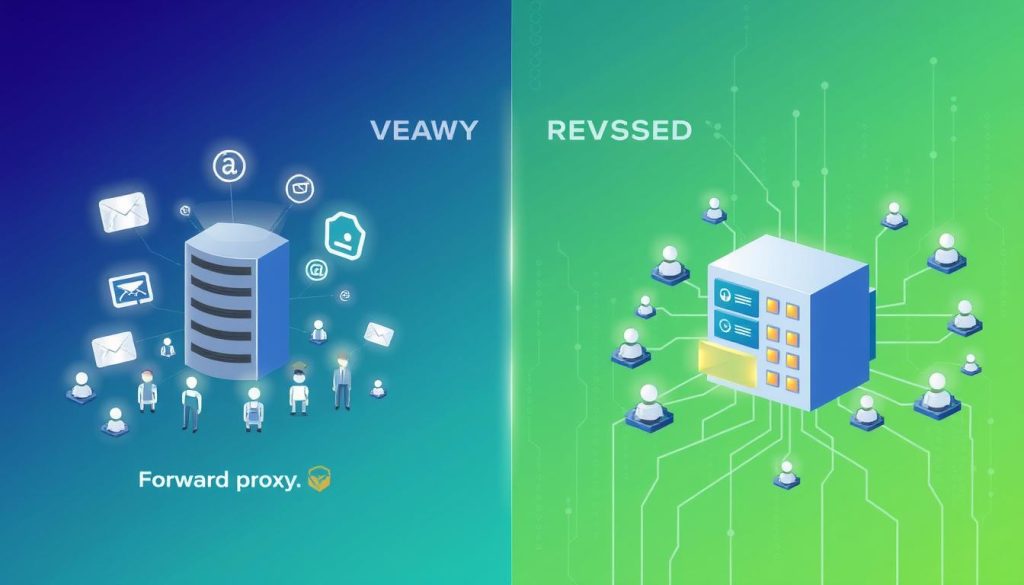
What is a Forward Proxy?
A forward proxy acts as a middleman between your devices and the internet. It makes requests on your behalf. This setup boosts privacy and filters content.
Definition and Basic Functionality
A forward proxy helps clients on private networks access the internet. It hides the client’s IP address by forwarding requests. This keeps the client’s identity secret.

How Forward Proxies Process Requests
Forward proxies get requests from clients and send them to the internet. They can change the request, like the client’s IP address, before sending it.
Popular Forward Proxy Technologies
Many forward proxy technologies exist, from open-source to commercial ones.
Open Source Solutions
Open-source options like Squid are flexible and customizable. They’re free and supported by the community.
Commercial Options
Commercial solutions offer more features and support. They’re great for big companies. Blue Coat and Forcepoint are examples.
When picking a forward proxy, think about scalability, security, and management. Make sure it fits your network needs.
What is a Reverse Proxy?
A reverse proxy is a server that sits between clients and web servers. It acts as an intermediary. It intercepts incoming client requests and forwards them to the right backend servers. This improves performance, security, and reliability.
Functionality and Request Processing
A reverse proxy is different from a forward proxy. It acts on behalf of servers, not clients. When a client sends a request, the reverse proxy decides which server to send it to.
This process boosts security by hiding the internal network. It also makes things more scalable and efficient.
Key benefits of using a reverse proxy include load balancing, SSL termination, and enhanced security. Load balancing spreads traffic across servers to avoid overload. SSL termination handles encryption and decryption, easing the load on servers.
Popular Reverse Proxy Technologies
Many technologies offer reverse proxy capabilities. They range from open-source to commercial options.
Open Source Solutions
- Nginx: Known for its high performance and scalability.
- Apache HTTP Server with mod_proxy: A versatile and widely-used solution.
- HAProxy: Specializes in load balancing and high availability.
Commercial Options
Commercial reverse proxy solutions offer extra features. They include advanced security and analytics. Examples are F5 BIG-IP and Citrix ADC.
| Feature | Nginx | HAProxy | F5 BIG-IP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Balancing | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SSL Termination | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Security Features | Limited | Limited | Advanced |

“A reverse proxy can significantly improve the security and performance of your web infrastructure by acting as an intermediary between clients and servers.”
Forward vs Reverse Proxy: Key Differences
It’s important to know the differences between forward and reverse proxies. They both act as middlemen but for different reasons. They work in different ways too.
Direction of Traffic Flow
A forward proxy sits between clients and the internet. It sends client requests to various servers online. On the other hand, a reverse proxy is between clients and servers. It directs client requests to the right server.
This difference in how traffic flows changes how each proxy is set up and used.
Client Awareness and Transparency
With a forward proxy, clients know they’re using a proxy. They set their browsers to use the proxy. This shows they’re choosing to go through the proxy.
But with a reverse proxy, clients don’t know they’re being proxied. The reverse proxy hides the server, making it seem like clients are talking directly to it.
Implementation Location
Forward proxies are often in a client’s network or on their premises. They manage outgoing traffic.
Reverse proxies are in front of servers, in data centers or the cloud. They handle incoming traffic.
Configuration Requirements
Setting up a forward proxy requires clients to configure their devices. They need to enter the proxy’s IP and port number.
Reverse proxies are set up on the server side. This means adjusting server settings or the proxy’s config files. It involves setting up routing and security.
Scalability Characteristics
Reverse proxies are built to handle lots of traffic. They can grow to meet more demand. They spread traffic across servers for better performance.
Forward proxies can scale too. But it depends on their use and the number of clients.
In summary, knowing the differences between forward and reverse proxies is key. Think about traffic flow, client awareness, where they’re used, how to set them up, and how they scale. This helps choose the right proxy for your needs.
Benefits of Using a Forward Proxy
Using a forward proxy can change how you see online privacy and security. It acts as a middleman between your device and the internet. This offers several key benefits that can make your online time better.
Enhanced Privacy and Anonymity
A forward proxy can greatly boost your online privacy by hiding your IP address. This makes it hard for websites and services to find out where you are. By using a proxy server, you can stay anonymous while surfing the web.
Access Control and Content Filtering
Forward proxies are also great for controlling what you can see online. Companies can block bad or non-work content. This helps keep things safe and productive. This is really helpful in schools and offices.
Bandwidth Optimization and Caching
Another big plus of forward proxies is saving bandwidth. They cache content you often visit. This means less bandwidth used, making websites load faster and your network work better.
Bypassing Geo-restrictions and Censorship
Forward proxies can also help you get around blocked content. By using a proxy in another area, you can see things you can’t normally. This is useful if you’re in a place with strict internet rules.
In short, forward proxies offer better privacy, control, bandwidth saving, and access to blocked content. They’re useful for anyone wanting to keep their online life safe or for companies wanting better network performance.
Benefits of Using a Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy can really change the game for your web apps. It acts as a middleman between clients and servers. This makes your web setup more scalable, secure, and fast.
Load Balancing Capabilities
One big plus of a reverse proxy is it spreads out traffic to many servers. This stops one server from getting too much work. Your users will see better speed and less lag.
SSL Termination and HTTPS Handling
A reverse proxy can handle SSL encryption and decryption. This lets your servers focus on what they do best. It also makes managing HTTPS certificates easier.
Security and DDoS Protection
Reverse proxies add an extra layer of security. They protect your servers from outside threats. They can also block DDoS attacks by filtering bad traffic.
Content Caching and Performance Acceleration
By caching often-used content, a reverse proxy makes web pages and apps load faster. This cuts down on server work and makes users happier.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Balancing | Distributes incoming traffic across multiple backend servers |
| SSL Termination | Handles SSL encryption and decryption, improving performance |
| Security | Provides an additional layer of security against external attacks |
| Content Caching | Caches frequently accessed content to accelerate delivery |
Common Use Cases for Forward Proxies
Forward proxies are very useful in many places. They help keep networks safe, control who can access them, and protect privacy. This is true in companies, schools, and when testing new things.
Corporate Networks and Access Control
In companies, forward proxies help manage the internet. They block bad websites and save often-used sites. This makes the network faster and safer by stopping threats.
Privacy-focused Browsing and VPN Integration
Forward proxies work well with VPNs to add more privacy and safety. This is great for people and groups who need to browse privately.
Content Filtering in Educational Institutions
Schools use forward proxies to control what websites are seen. They block sites that are not good for learning. This keeps students focused and follows rules.
Development and Testing Environments
In testing, forward proxies are helpful. They mimic different networks, save resources, and test how apps work in different situations.
Knowing how forward proxies are used helps us see their value. They make networks safer, control access, and help with privacy and testing.
Common Use Cases for Reverse Proxies
Reverse proxies are very useful in many web applications. They help make your web infrastructure more secure, faster, and scalable.
Web Application Hosting and Security
Reverse proxies add an extra layer of security for web hosting. They hide your backend servers’ IP addresses. They also handle SSL termination.
API Gateway Implementation
A reverse proxy can act as an API gateway. It manages API requests, routes them, and handles tasks like authentication and rate limiting.
Microservices Architecture Support
In microservices architecture, reverse proxies simplify things. They route requests to the right microservices, making the infrastructure easier to manage.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Reverse proxies are key in CDNs. They cache content at edge locations. This reduces latency and speeds up content delivery for users everywhere.
Knowing these use cases helps you see the value of reverse proxies. They enhance security, performance, and scalability in your web infrastructure.
Implementation Considerations
When setting up a proxy server, you need to think about a few important things. These help make sure your proxy works well and keeps your data safe. You’ll need to look at different factors to see how well your proxy will do.
Hardware vs Software Solutions
You can pick between hardware and software proxy options. Hardware is strong and fast but costs a lot at first. Software is cheaper and more flexible.
| Feature | Hardware Solutions | Software Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | High | Variable |
| Cost | High upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Flexibility | Limited | High |
Cloud-based Proxy Services
Cloud-based proxy services are great because they grow with you. They mix the good parts of hardware and software without needing a big setup.
Performance Impact and Latency Concerns
Adding a proxy server can change how your network works. You should think about how it affects speed and try to make it better.
Security Implications and Best Practices
Proxy servers can be risky if not set up right. Use encryption, controls, and check for security issues often to stay safe.
How to Choose Between Forward and Reverse Proxy
Choosing between a forward proxy and a reverse proxy depends on your network and security needs. You must understand your specific needs and how each proxy works.
Assessing Your Specific Network Requirements
First, think about what your network needs. If you want to control outgoing traffic or keep your users’ identities hidden, a forward proxy might be best. But, if you need to secure and speed up incoming traffic, a reverse proxy is better.
Scalability and Performance Needs
Next, think about how big your network needs to be and how fast it should run. Reverse proxies help spread out traffic, making your network more scalable and less loaded.
Security Priorities and Compliance Requirements
Security is key. Forward proxies hide your internal network’s IP addresses, while reverse proxies hide your servers’ IP addresses from the outside world.
Budget and Resource Constraints
Don’t forget about money and resources. Look at the costs of setting up and keeping either proxy running. This includes hardware, software, and people costs.
Implementation Complexity and Maintenance
Lastly, think about how hard it will be to set up and keep your proxy running. Make sure your team has the skills and resources to handle it.
By looking at these points, you can decide if a forward or reverse proxy is best for you.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between forward and reverse proxies is key. Both types have their own uses and benefits. When choosing, think about what you need, like traffic direction and scalability.
Doing a proxy server comparison helps you decide wisely. By looking at your needs and each proxy’s strengths, you pick the best one. Whether it’s for privacy, security, or performance, the right proxy is crucial.